Who Owns Eli Lilly: The Largest Shareholders Overview

Eli Lilly and Company (LLY) is one of the largest drug manufacturers in the world and started as a family business. It makes money predominantly from drugs treating diabetes, but Eli Lilly also has successful oncology and immunology products. Let’s look at who owns Eli Lilly and who controls it.
Eli Lilly’s largest shareholders are a non-profit organization Lilly Endowment, which owns a 10.8% share, followed by Vanguard (7.7%), BlackRock (6.9%) and, interestingly, also PNC Financial Services (5.5%). Most of the PNC stake results from being a trustee of Eli Lilly’s compensation trust.
|
|
|||
| Shareholder | Ownership | Voting Power | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lilly Endowment | 10.8% | 10.8% | |
| Vanguard | 7.7% | 7.7% | |
| BlackRock | 6.9% | 6.9% | |
| PNC Financial Services | 5.5% | 5.5% | |
| Other | 69.1% | 69.1% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | |||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
|||
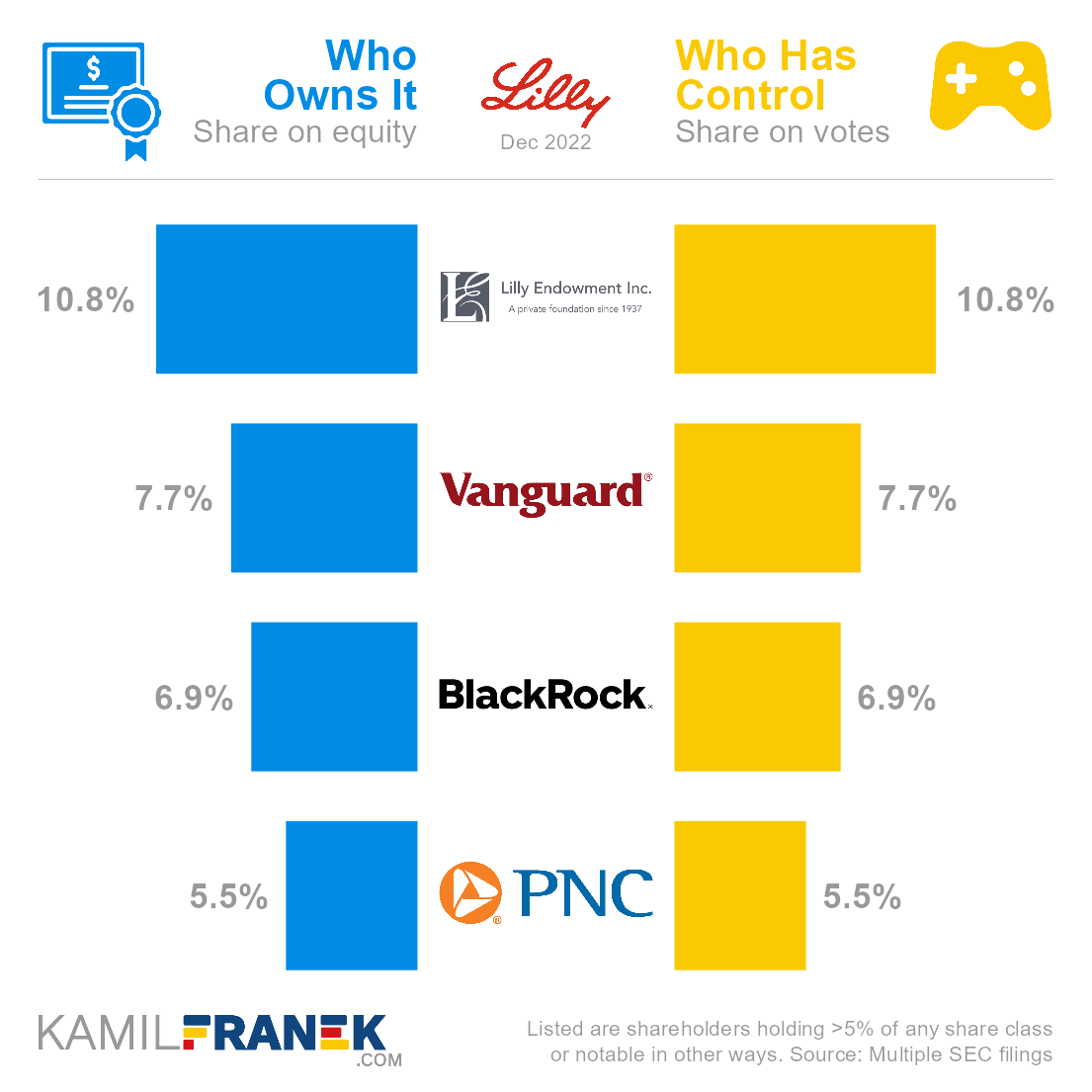
In this article, I will dive more into who owns Eli Lilly and who controls it. I will show you who Eli Lilly’s largest shareholders are, how many shares and votes they have, and how much their stake is worth.
If you are interested, you can also explore who owns other companies like Walmart, Apple, UnitedHealth, and other articles in my “Who Owns Who” series.
📃 Who Owns Eli Lilly?
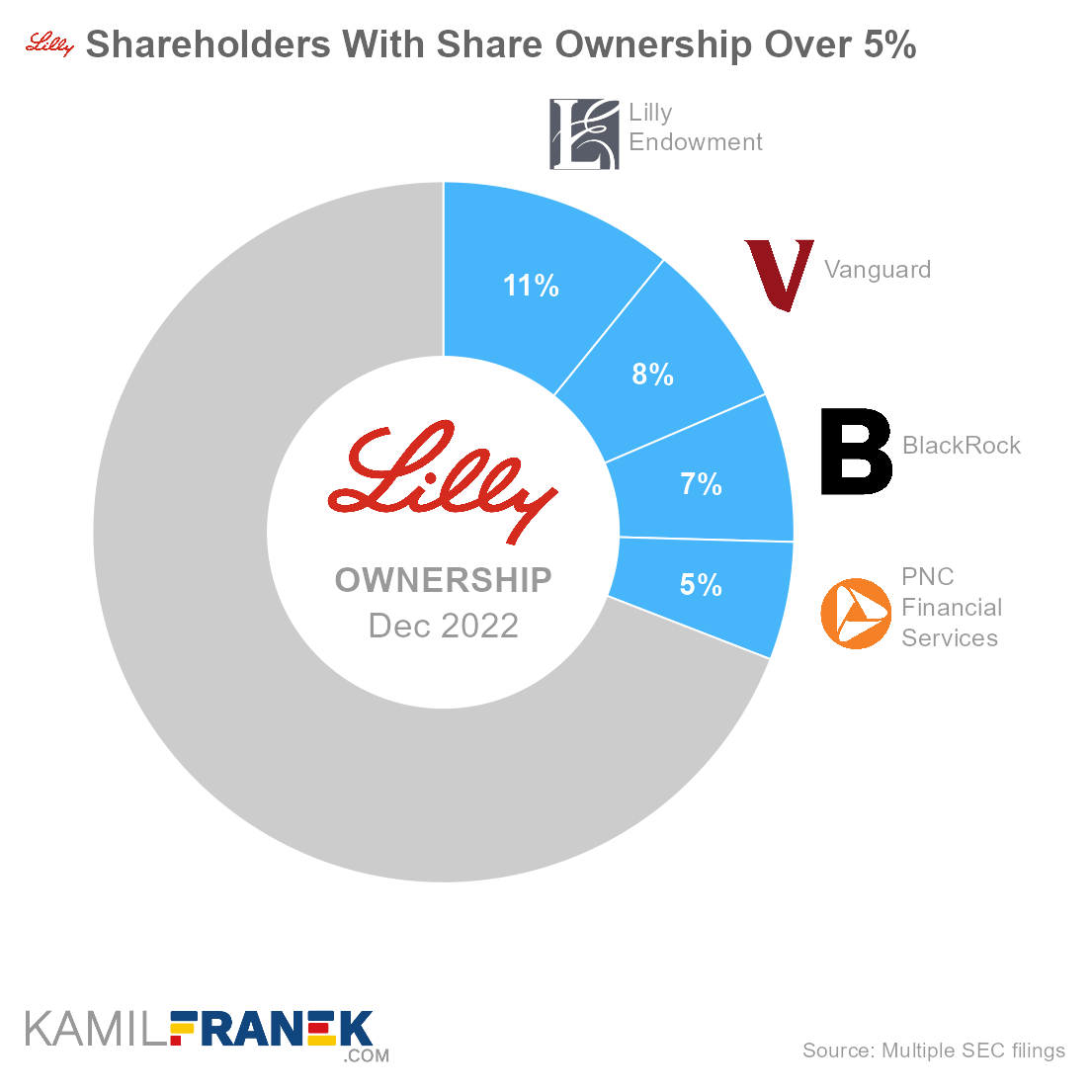
Eli Lilly is owned by its shareholders. The largest one is a non-profit organization Lilly Endowment set up by Eli Lilly’s founder, which owns 10.8% of the company. It is followed by asset manager giants Vanguard (7.7%) and BlackRock (6.9%). A large shareholder is formally also PNC.
The largest owner of Eli Lilly is a non-profit organization Lilly Endowment, which owns 10.8% of the company.
- Lilly Endowment is a not-for-profit corporation established in 1937 by Josiah K. Lilly Sr. and his sons. Josiah K. Lilly Sr. was the son of the company founder Colonel Eli Lilly.
- Although Lilly Endowment’s history is tied to the founding family of Eli Lilly and Company, it is currently run independently.
- Lilly Endowment is independent, but most of its funds are invested in Eli Lilly’s stocks, and it is one of the “defense” barriers that discourage takeover attempts.
The second and third largest Eli Lilly owners are asset management giants Vanguard, which owns a 7.7% stake, and BlackRock, with a 6.9% ownership share.
- Vanguard and BlackRock are the largest asset managers worldwide, and it is common to see them among top shareholders in large public companies, especially if they lack other direct shareholders.
- However, these are not their money. They invest it on behalf of other investors.
The fourth-largest owner of Eli Lilly is PNC Financial Services, which owns 5.5% of the company.
- It can be surprising to see PNC among the largest owners. It is one of the largest US banks, but its asset management business is quite small to justify such a large stake.
- By digging deeper into company fillings, we can see the vast majority of this stake is a result of PNC’s acting as directed trustee of Eli Lilly’s Compensation Trust.
Eli Lilly was founded in 1876 by Colonel Eli Lilly and has been a publicly listed company since its initial public offering on NYSE in 1952 (Ticker: LLY).
Eli Lilly and Company is incorporated in the State of Indiana (US), and its headquarters are in Indianapolis, Indiana (US).
🎮 Who Controls Eli Lilly (LLY)?
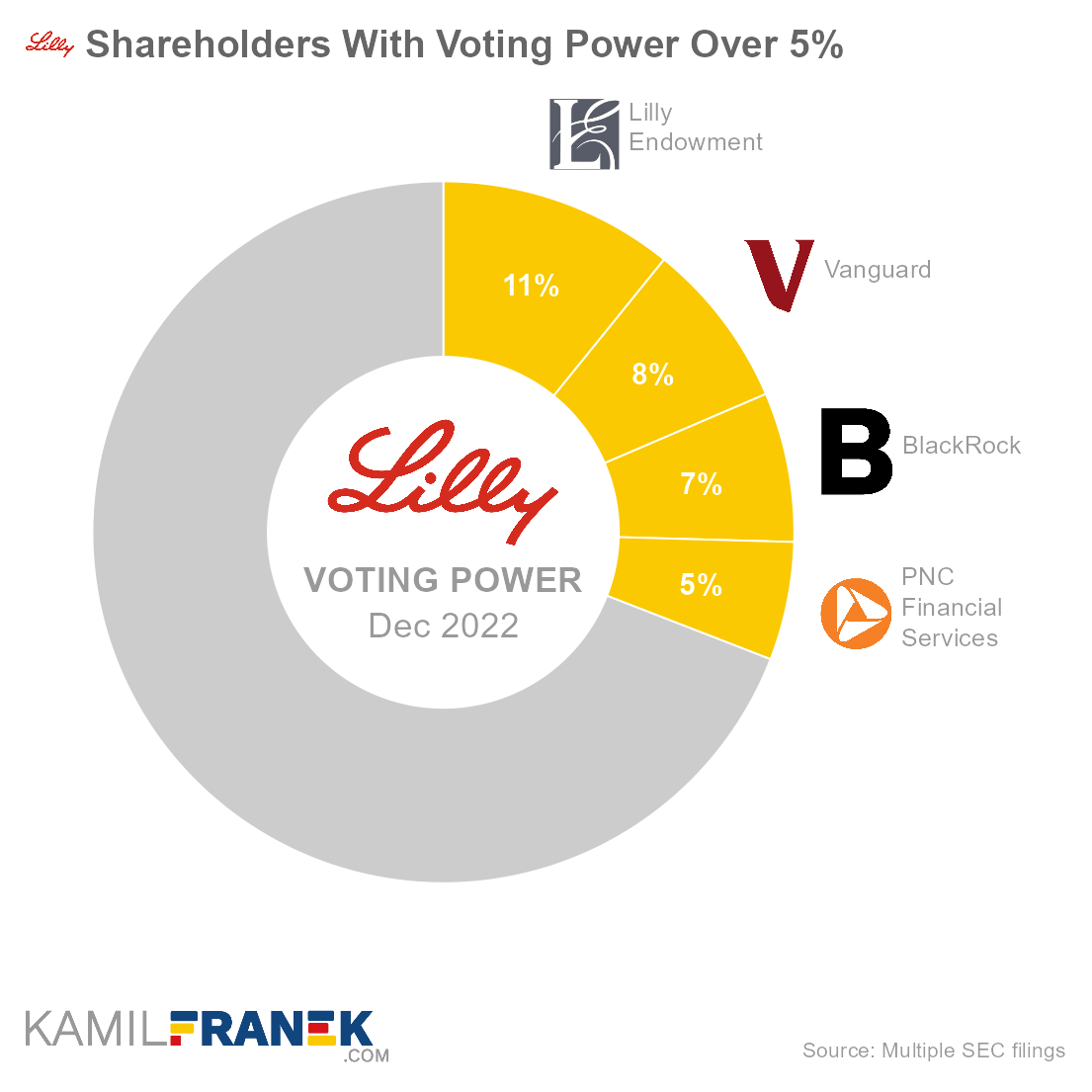
Eli Lilly’s shareholders with the largest voting power are Lilly Endowment, which holds 10.8% of all votes, followed by asset managers Vanguard (7.7%) and BlackRock (6.9%). Large voting power also holds PNC Financial Services acting as a trustee of Eli Lilly’s Compensation Trust.
Eli Lilly has only one class of outstanding shares, with one vote per share. Therefore, there is no difference between the shareholder’s ownership and voting power.
Eli Lilly’s shareholder with the largest voting power is a non-profit organization Lilly Endowment which holds 10.8% of all votes.
- Lilly Endowment is an independent not-for-profit corporation, formally independent from Eli Lilly and Company.
- However, despite its independence, it has a huge part of its portfolio tied in Eli Lilly’s shares, and it is considered to be friendly to company management proposals.
- The existence of this stake makes it harder for outsiders to attempt to take over the company, which gives company insiders more power.
Eli Lilly’s shareholders with the second and third largest voting power are Vanguard (7.7%) and BlackRock (6.9%) which together hold 14.6% of all votes.
- Significant ownership by large asset managers that usually support management proposals creates conflicts of interest between Eli Lilly’s management, asset manager’s management, and the ultimate underlying investors that asset managers represent.
Eli Lilly’s shareholder with the fourth-largest voting power is PNC Financial Services, holding 5.5% of all votes.
- As mentioned before, most of this stake represents shares within Eli Lilly’s Compensation Trust, where PNC acts as a trustee.
- This Trust is another part of protection against the takeover of the company because more shares are “parked” in management-friendly entities.
None of the top shareholders has individual control over the company. The four top shareholders together represent 30.9% of the voting power.
- All of the top shareholders have in common that they will probably act in line with the company insiders and support their proposals.
Eli Lilly’s insiders that have influence over the company are CEO and chairman David Ricks and other board members and executives.
- The power the insiders have is extensive because of the ownership structure full of passive management-friendly entities.
- Eli Lilly’s articles of incorporation and ByLaws contain other provisions that give even more power to insiders and make it hard for outsiders to take over the company.
- Eli Lilly’s board of directors consists of 12 members. The company has a classified board, separated into 3 groups with 3-year terms. Therefore only 1/3 of the directors are up for reelection each year, making it hard to change the course of the company quickly.
- Another antitakeover provision is that unless Board approves a takeover or merger, it requires 80% of votes at a shareholder meeting, which can be hard given the company’s ownership structure.
🗳️ Breakdown of Eli Lilly’s Outstanding Shares and Votes by Top Shareholders
Eli Lilly and Company had a total of 951 million outstanding shares as of December 2022. The following table shows how many shares each Eli Lilly’s large shareholder holds.
|
|
||||
| In millions of shares as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lilly Endowment | 102.9 | 102.9 | 10.8% | |
| Vanguard | 73.4 | 73.4 | 7.7% | |
| BlackRock | 65.5 | 65.5 | 6.9% | |
| PNC Financial Services | 51.8 | 51.8 | 5.5% | |
| Other | 657.0 | 657.0 | 69.1% | |
| Total (# millions) | 950.6 | 950.6 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
||||
There were 951 million votes distributed among shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. The table below shows the total number of votes for each large shareholder.
|
|
||||
| In millions of votes as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lilly Endowment | 102.9 | 102.9 | 10.8% | |
| Vanguard | 73.4 | 73.4 | 7.7% | |
| BlackRock | 65.5 | 65.5 | 6.9% | |
| PNC Financial Services | 51.8 | 51.8 | 5.5% | |
| Other | 657.0 | 657.0 | 69.1% | |
| Total (# millions) | 950.6 | 950.6 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
||||
💵 Breakdown of Eli Lilly’s Market Value by Shareholder
The following table summarizes how much is each shareholder’s stake in Eli Lilly and Company worth.
However, keep in mind that a stake in Eli Lilly could be just one part of their portfolio, and their total worth could be bigger, thanks to other investments. It could also be lower if they have debts.
|
|
||||
| Market value in billions $ as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lilly Endowment | $37.7 | $37.7 | 10.8% | |
| Vanguard | $26.9 | $26.9 | 7.7% | |
| BlackRock | $24.0 | $24.0 | 6.9% | |
| PNC Financial Services | $19.0 | $19.0 | 5.5% | |
| Other | $240.3 | $240.3 | 69.1% | |
| Total ($ billions) | $347.8 | $347.8 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
||||
Let’s now look at each Eli Lilly shareholder individually.
📒 Who Are Eli Lilly’s Largest Shareholders?
Let’s now go through the list of the largest shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company one by one and look at who they are, how many shares they own, what is their voting power, and how much is their stake in Eli Lilly worth.
#1 Lilly Endowment (10.8%)
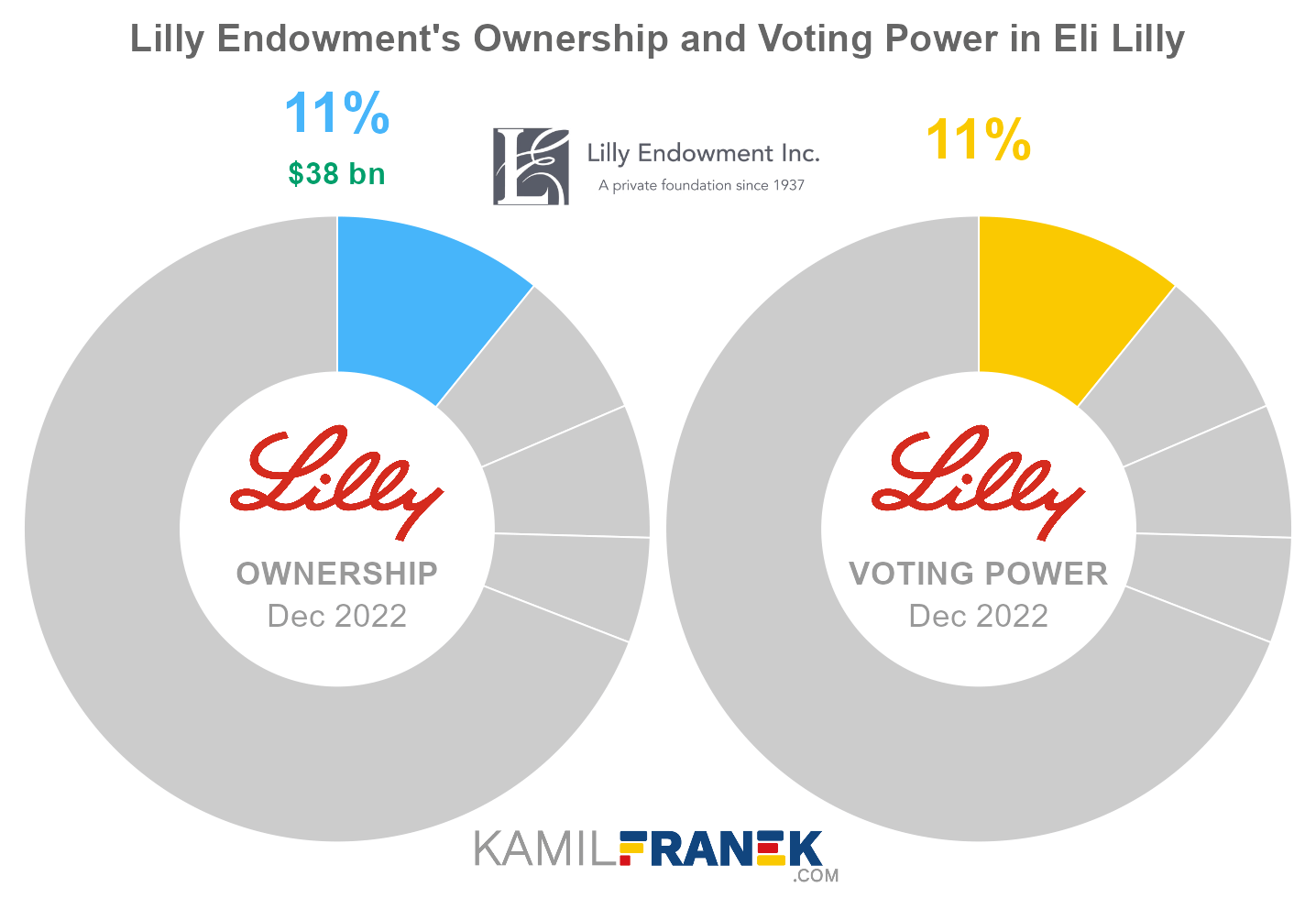
Lilly Endowment is the largest shareholder of Eli Lilly, owning 10.8% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of Lilly Endowment’s stake in Eli Lilly was $37.7 billion.
Lilly Endowment owned 103 million shares in Eli Lilly and controlled 103 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
Lilly Endowment Inc. is a not-for-profit corporation, established in 1937 by Josiah K. Lilly Sr. and his sons.
The organization’s grants focus on community development, education, and religion, with many located in Indianapolis and the state of Indiana.
Josiah K. Lilly Sr. was the son of Colonel Eli Lilly, founder of Eli Lilly and Company, and the Lilly family donated a sizable amount of company stock to the Endowment.
Over the past 82 years, Lilly Endowment has donated nearly $10.9 billion to 10,048 charitable organizations. It had assets totaling nearly $17 billion at the end of 2019.
#2 Vanguard (7.7%)
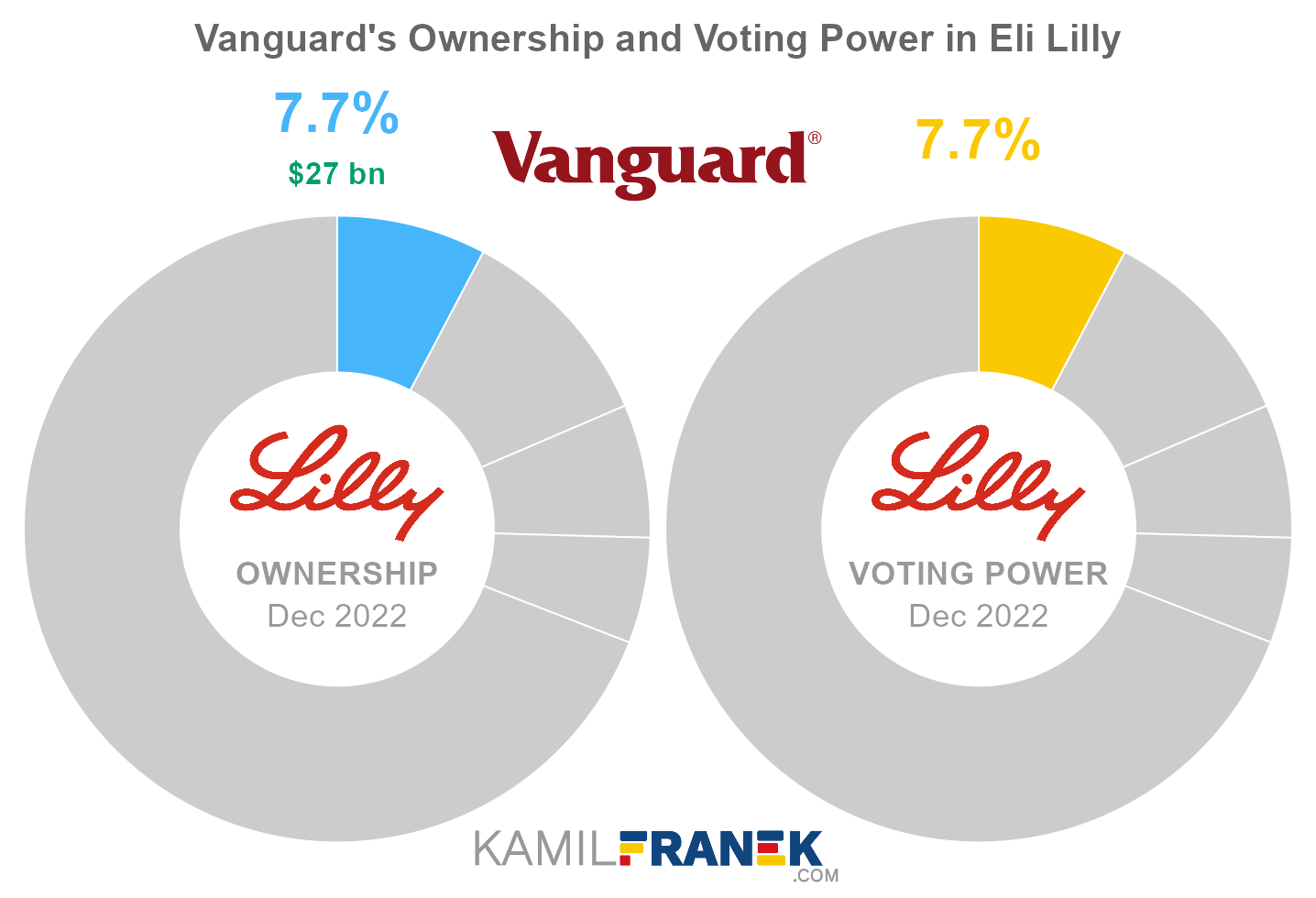
Vanguard is the second-largest shareholder of Eli Lilly, owning 7.7% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of Vanguard’s stake in Eli Lilly was $26.9 billion.
Vanguard owned 73 million shares in Eli Lilly and controlled 73 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
Vanguard (The Vanguard Group) is one of the largest asset managers in the world. It manages other people’s money through its mutual funds and exchange-traded funds and also offers other related investing and financial planning services.
Vanguard differs from other large asset managers by having no actual “owner .” Officially Vanguard says that its investors own it since its funds own it, and Vanguard fund investors own those funds.
However, the actual decision power is in the hands of Vanguard’s insiders since the ownership is diluted over millions of investors worldwide.
Vanguard has significant influence over the largest public companies. Thanks to its size, Vanguard usually belongs to the largest shareholders in those companies and has considerable power at their shareholder meetings. This is especially true if ownership is diluted.
- Several terms were coined to describe this issue. Some call it asset manager capitalism, and popular is also the power of twelve. Financial Times even put together who exactly those twelve people might be.
- Evidence shows that big asset managers usually vote together with management.
#3 BlackRock (6.9%)
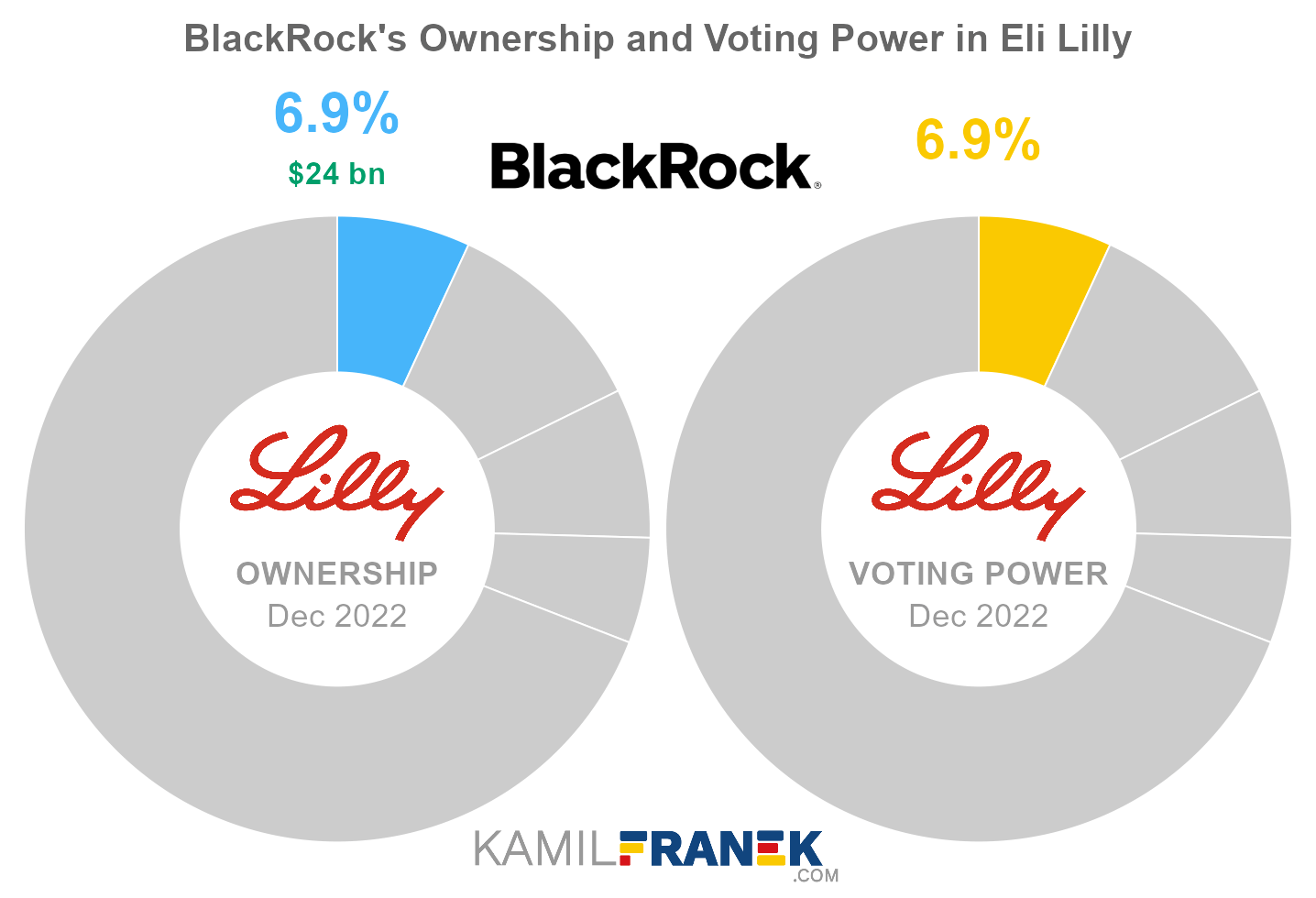
BlackRock is the third-largest shareholder of Eli Lilly, owning 6.9% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of BlackRock’s stake in Eli Lilly was $24.0 billion.
BlackRock owned 65 million shares in Eli Lilly and controlled 65 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
BlackRock, Inc. is the world’s largest asset manager, with assets under management of $10 trillion. BlackRock is not only an asset manager, but it also provides other asset managers and corporations with its Aladdin portfolio management software.
BlackRock is a publicly traded company, and its largest shareholders are its competitors, including BlackRock itself. Not directly but through their passive and active funds. The largest shareholder is Vanguard.
A similar situation is also true in the opposite direction because BlackRock is a significant shareholder in many of its publicly traded competitors and other large institutions, making the whole thing even more eyebrow-raising.
This circular ownership between Vanguard, BlackRock, and other large asset managers, amplifies the issue often raised about the power of these large asset managers over public companies since they usually belong to the most significant shareholders with large voting power.
-
In the case of Blackrock, this influence is personified in the form of its CEO Larry Fink, who is a powerful figure with close ties to the FED and the US government.
-
Adding to these concerns is evidence that BlackRock and other asset managers usually vote in favor of management proposals.
#4 PNC Financial Services (5.5%)
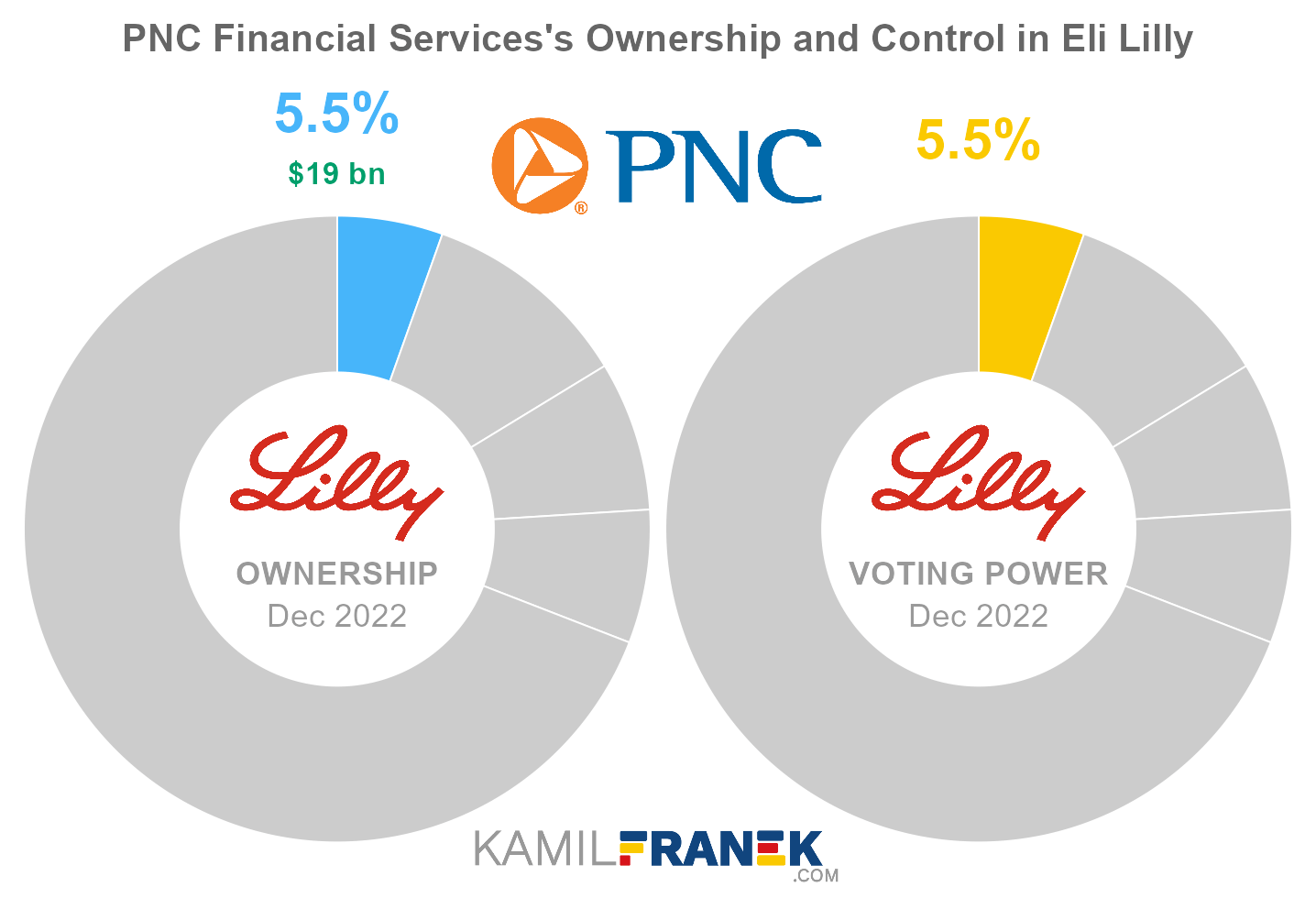
PNC Financial Services owns 5.5% of Eli Lilly’s shares. As of December 2022, the market value of PNC Financial Services’s stake in Eli Lilly was $19.0 billion.
PNC Financial Services owned 52 million shares in Eli Lilly and controlled 52 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
The PNC Financial Services Group is an American bank holding company and financial services corporation based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It is one of the largest banks in the US. Its business focus is mainly retail banking and corporate and institutional banking, but it also has a smaller asset management business.
🧱 Who and When Founded Eli Lilly?
Eli Lilly and Company was founded in 1876 by a veteran of the American Civil War and a pharmaceutical chemist Colonel Eli Lilly.
One of Lilly’s first drugs was “quinine”, which was used to treat malaria. As the company grew, it continued to develop new products and expand its operations. In 1881, Eli Lilly and Co. became a corporation.
One of the early employees was also Lilly’s son Josiah (J. K.), and a few years later, Lili’s brother worked for him as a salesman. Eli Lilly’s growing business later employed also other Lilly family members, so to a certain extent, it was a family business.
Eli Lilly’s first widely successful product was Succus Alteran (1883). Sales from this product provided the company with the funds to expand its manufacturing and research.
The company continued to grow, and in 1890 Colonel Eli Lilly turned over much of the company’s management to his son, Josiah K. Lilly Sr.
In 1898, Josiah K. Lilly Sr. took over the company entirely after his father’s death.
By 1905, Eli Lilly and Co. had hit $1 million in sales, a significant milestone at the time.
Eli Lilly’s most famous products are probably Prozac and Cymbalta for clinical depression and Zyprexa for antipsychotic treatment.
However, today the main source of its revenue are products to treat diabetes, such as Trulicity.
📅 Eli Lilly’s History Timeline
These are selected events from Eli Lilly’s history:
- 1876: Eli Lilly and Company, a drug manufacturing venture, was founded by Colonel Eli Lilly, a pharmaceutical chemist, and veteran of the American Civil War
- 1881: Eli Lilly and Co. became a corporation.
- 1890: Colonel Eli Lilly turned over much of the management of the company to his son, Josiah K. Lilly Sr.
- 1898: Josiah K. Lilly Sr. took over the company completely after his father died.
- 1901: The company was incorporated in Indiana to succeed the original business
- 1905: Lilly hit $1 million in sales.
- 1917: Lilly set up a medical field hospital in France to treat wounded soldiers of all nationalities during World War I.
- 1919: Eugene N. Beesley was appointed as the first non-family president of Lilly.
- 1922: Clowes and Eli Lilly agreed with Toronto researchers J. J. R. Macleod, Frederick G. Banting, and Charles H. Best to mass-produce insulin.
- 1923: Lilly introduced Iletin (animal-source insulin), the world’s first commercially available insulin product, for the treatment of diabetes.
- 1928: Lilly introduced a liver-extract product to treat pernicious anemia, a life-threatening blood disorder.
- 1932: Josiah K. Lilly Sr. remained as chairman but handed over presidency to his son Eli Lilly Jr.
- 1934: The first overseas subsidiary was established in England.
- 1937: Josiah K. Lilly Sr. and his sons founded the Lilly Endowment with a sizable initial donation in company stocks.
- 1945: Lilly manufactured more than two million pints of blood plasma and two hundred military products during World War II.
- 1948: Chairman Josiah K. Lilly, son of the founder, died. Eli Lilly Jr., the founder’s grandson, retired from active management of the company, became chairman of the board and relinquished the presidency to his brother, Josiah K. Lilly, Jr.
- 1952: The company offered its first public shares of stock.
- 1953: Eugene N. Beesley was named the company’s new president, the first non-family member to run the company.
- 1955: Lilly was the first company to manufacture and distribute the Salk Polio Vaccine globally.
- 1957: Darvon, a non-addictive pain medication, was launched.
- 1958: Lilly introduced Vancocin, an antibiotic for infections associated with certain types of resistant bacteria.
- 1961: Velban, the company’s first oncology drug, was introduced for the treatment of several types of cancer.
- 1964: Keflin was launched, maintaining Lilly’s lead in antibiotics.
- 1971: To further diversify its product line, Lilly diversified into other areas, most notably agricultural chemicals, animal-health products, cosmetics, and medical instruments.
- 1972: Richard Donald Wood became Lilly’s president and CEO after the retirement of Burton E. Beck.
- 1977: Lilly acquired Cardiac Pacemakers Incorporated, a manufacturer of heart pacemakers.
- 1977: Lilly acquired IVAC Corporation, which manufactures vital signs and intravenous fluid infusion monitoring systems.
- 1980: Lilly acquired Physio-Control Corporation.
- 1982: Lilly introduced Humulin, insulin identical to that produced by the human body.
- 1984: Lilly acquired Advance Cardiovascular Systems Incorporated.
- 1986: Lilly introduced Prozac in Belgium to treat clinical depression.
- 1986: Prozac (fluoxetine) was launched and became one of Eli Lilly’s most successful drugs.
- 1986: Lilly acquired Hybritech.
- 1987: Prozac was approved by the U.S. FDA for use in treating depression.
- 1989: Lilly acquired Devices for Vascular Intervention Incorporated.
- 1990: Lilly acquired Pacific Biotech.
- 1991: Vaughn Bryson became president and CEO, and Wood became board chairman.
- 1992: Lilly acquired Origin Medsystems and Heart Rhythm Technologies Incorporated.
- 1993: Randall L. Tobias was named chairman, president, and CEO. Tobias was recruited from outside the company’s executive ranks to replace Lilly’s president and CEO, Vaughn Bryson.
- 1994: Lilly acquired PCS Health Systems Inc., a manager of prescription drug benefits.
- 1994: Applied Molecular Evolution Inc. was acquired by the company to use its technology to speed up the discovery of biological drugs.
- 1996: Lilly introduced Zyprexa for the treatment of schizophrenia.
- 1996: Lilly introduced Gemzar, a drug for the treatment of pancreatic and non-small-cell lung cancer.
- 1996: Eli Lilly launches Humalog, its diabetes drug.
- 1998: Sidney Taurel, former chief operating officer of Lilly, was named CEO to replace Tobias, who retired. Taurel became chairman of the board in January 1999.
- 1999: Actos was launched for diabetes.
- 2001: Lilly lost its U.S. patent protection for Prozac.
- 2002: The company received FDA approval for two new drugs, Forteo and Strattera.
- 2003: Eli Lilly introduced Cialis (tadalafil), a competitor to Pfizer’s blockbuster Viagra for erectile dysfunction.
- 2004: Eli Lilly launches depression drug Cymbalta (duloxetine).
- 2005: John C. Lechleiter became Lilly’s president and chief operating officer.
- 2005: The company agreed to pay $36 million in connection with the illegal promotion of Evista.
- 2006: Lilly paid $700 million to settle around 8,000 lawsuits related to antipsychotic medication Zyprexa and, in early 2007, paid $500 million to settle around 18,000 other lawsuits.
- 2006: Lilly bought Icos Corporation in order to gain full control of Cialis (tadalafil).
- 2007: Evista, a drug that helps reduce the risk of invasive breast cancer, was introduced by the company after FDA approval.
- 2008: The company acquired the cancer-drug maker ImClone Systems for $6.5bn.
- 2008: Cialis, used to treat male sexual function problems, was launched by the company.
- 2008: John C. Lechleiter was elected as Lilly’s CEO and president.
- 2008: Eli Lilly purchased the right to manufacture controversial bovine growth hormone from Monsanto.
- 2008: Sidney Taurel retired as CEO but remained as chairman of the board until 31 December.
- 2009: Effient, a drug used to prevent blood clots in heart disease patients, was launched by the company.
- 2009: Eli Lilly pleaded guilty to a US federal criminal misdemeanor charge of illegally marketing Zyprexa and paid a $1.415 billion penalty.
- 2011: Lilly partnered with Boehringer Ingelheim to develop and market Tradjenta, which lowers blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes.
- 2011: Zyprexa’s patent expired.
- 2013: Cymbalta’s patent expired, which led to a large loss in sales.
- 2013: Eli Lilly sued Canada for violating its obligations to foreign investors under NAFTA by allowing its courts to invalidate patents for Straterra and Zyprexa.
- 2014: Jardiance and Trulicity were launched, which are drugs aimed at the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
- 2014: Eli Lilly launches diabetes drug Trulicity (dulaglutide).
- 2014: Lilly announced plans to buy Swiss drugmaker Novartis AG’s animal health business for $5.4 billion.
- 2017: Lilly acquired CoLucid Pharmaceuticals for $960 million.
- 2017: Lilly and Shionogi jointly licensed their product varespladib to Ophirex for the latter’s novel snakebite treatment program.
- 2018: Lilly acquired Armo Biosciences for $1.6 billion.
- 2019: The company debuted a generic version of Humalog to provide a lower-cost option.
- 2019: Lilly announced it would acquire Loxo Oncology for around $8 billion.
- 2019: Lawmakers from the United States House of Representatives sent letters to Eli Lilly and other insulin manufacturers asking for explanations for their rapidly raising insulin prices.
- 2020: Lilly developed a COVID-19 single antibody treatment called bamlanivimab and received approval from the FDA through an emergency-use authorization.
- 2020: Lilly announced its acquisition of Dermira for $1.1 billion.
- 2020: Lilly partnered with Amgen to manufacture their COVID-19 antibody therapies.
- 2020: Lilly announced it would acquire Disarm Therapeutics
- 2020: Lilly announced it would acquire Prevail Therapeutics Inc for $1 billion, boosting its pipeline in neurodegenerative disease gene therapies.
- 2021-04: FDA revoked the emergency use authorization for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab, when administered alone, to be used for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and certain pediatric patients.
- 2021-05: FDA had accepted Lilly’s application for Tyvyt (sintilimab), in combination with Lilly’s own Alimta (pemetrexed) and platinum chemotherapy for newly diagnosed nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer.
- 2022: A parody Twitter account’s false announcement about insulin sales ending in November 2022 wiped $20 billion of the company’s market value.
- 2022: Distribution of Lilly’s COVID-19 antibody drug was paused due to a lack of efficacy against the emerging omicron variant.
- 2022-02: A second COVID-19 monoclonal antibody therapy (bebtelovimab) developed with AbCellera was given Emergency Use Authorization, with the U.S. Government committing to a $720 million purchase of up to 600,000 doses.
- 2022-11: Eli Lilly announced that it would be reducing the out-of-pocket price of insulin to $35 a month and lowering the price of Humalog.
📚 Recommended Articles & Other Resources
Who Owns Tesla: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Tesla and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns JPMorgan Chase: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns JPMorgan Chase and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Walmart: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Walmart and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Apple: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Visual overview of who owns Apple and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Nestlé: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Nestlé and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Saudi Aramco: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Saudi Aramco and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Other Resources
- Eli Lilly’s Annual Financials Statements (K-10)
- Eli Lilly’s Proxy Statement
- Eli Lilly’s Certificate of Incorporation
Disclaimer: Although I use third-party trademarks and logos in this article and its visuals, kamilfranek.com is an independent site, and there is no relationship, sponsorship, or endorsement between this site and the owners of those trademarks.

