Who Owns Saudi Aramco: The Largest Shareholders Overview

Saudi Arabian Oil Company (SR:2222) is the largest oil and gas company in the world, making money mainly from extracting oil and also from refining and petrochemicals. Let’s look at who owns Saudi Aramco and who controls it.
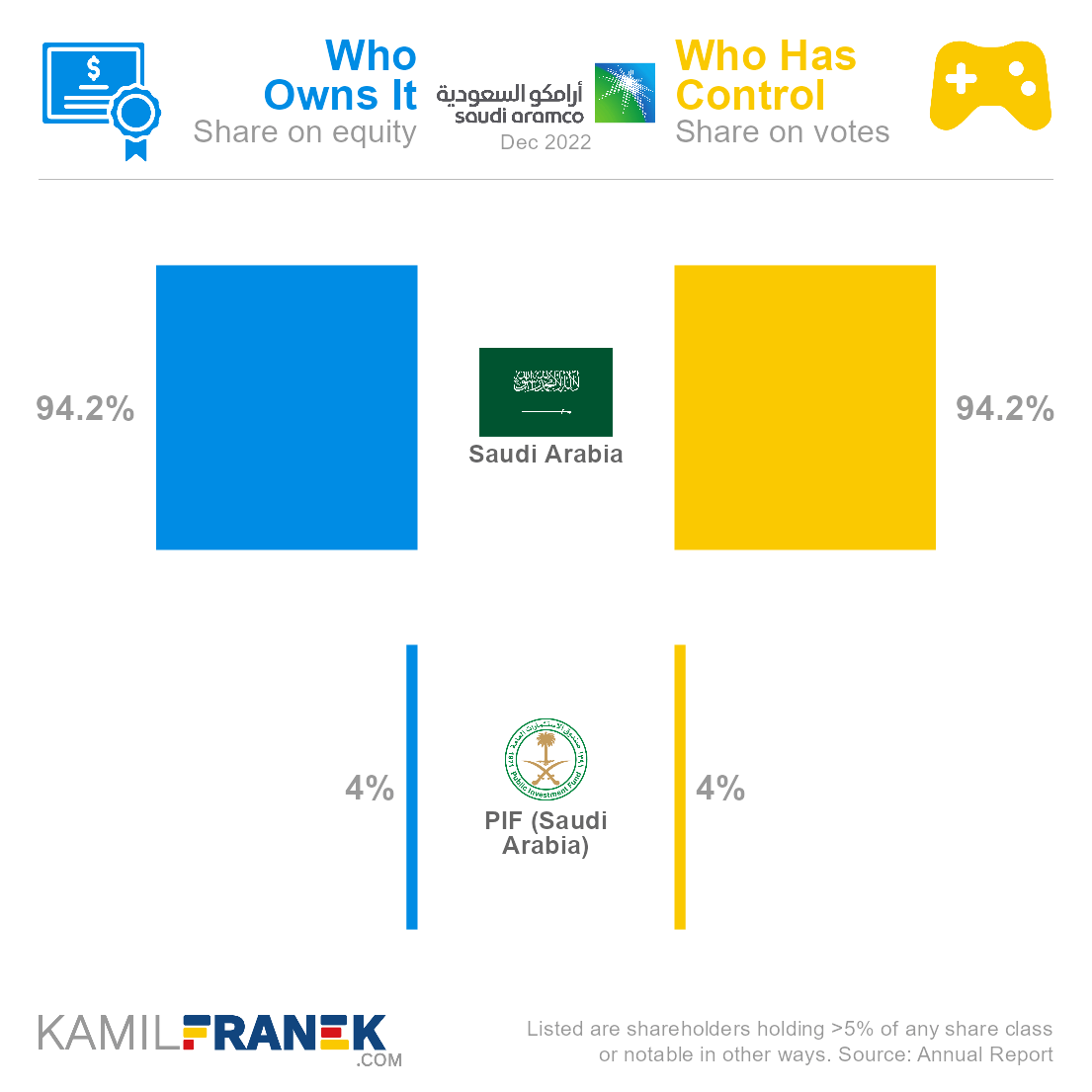
Saudi Aramco’s largest and dominant shareholder is the Saudi Arabia government, which owns 94.2% share, followed by Public Investment Fund, Saudi Arabia sovereign wealth fund, which owns another 4.0%. When added together, the Saudi government controls 98.2% of the company.
|
|
|||
| Shareholder | Ownership | Voting Power | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 94.2% | 94.2% | |
| PIF (Saudi Arabia) | 4.0% | 4.0% | |
| Other | 1.8% | 1.8% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | |||
 Source: Annual Report Source: Annual Report |
|||
In this article, I will dive more into who owns Saudi Aramco and who controls it. I will show you who Saudi Aramco’s largest shareholders are, how many shares and votes they have, and how much their stake is worth.
If you are interested, you can also explore who owns other companies like Microsoft, Exxon Mobil, Lenovo, Volkswagen, Shell, and other articles about who owns who.
📃 Who Owns Saudi Aramco?
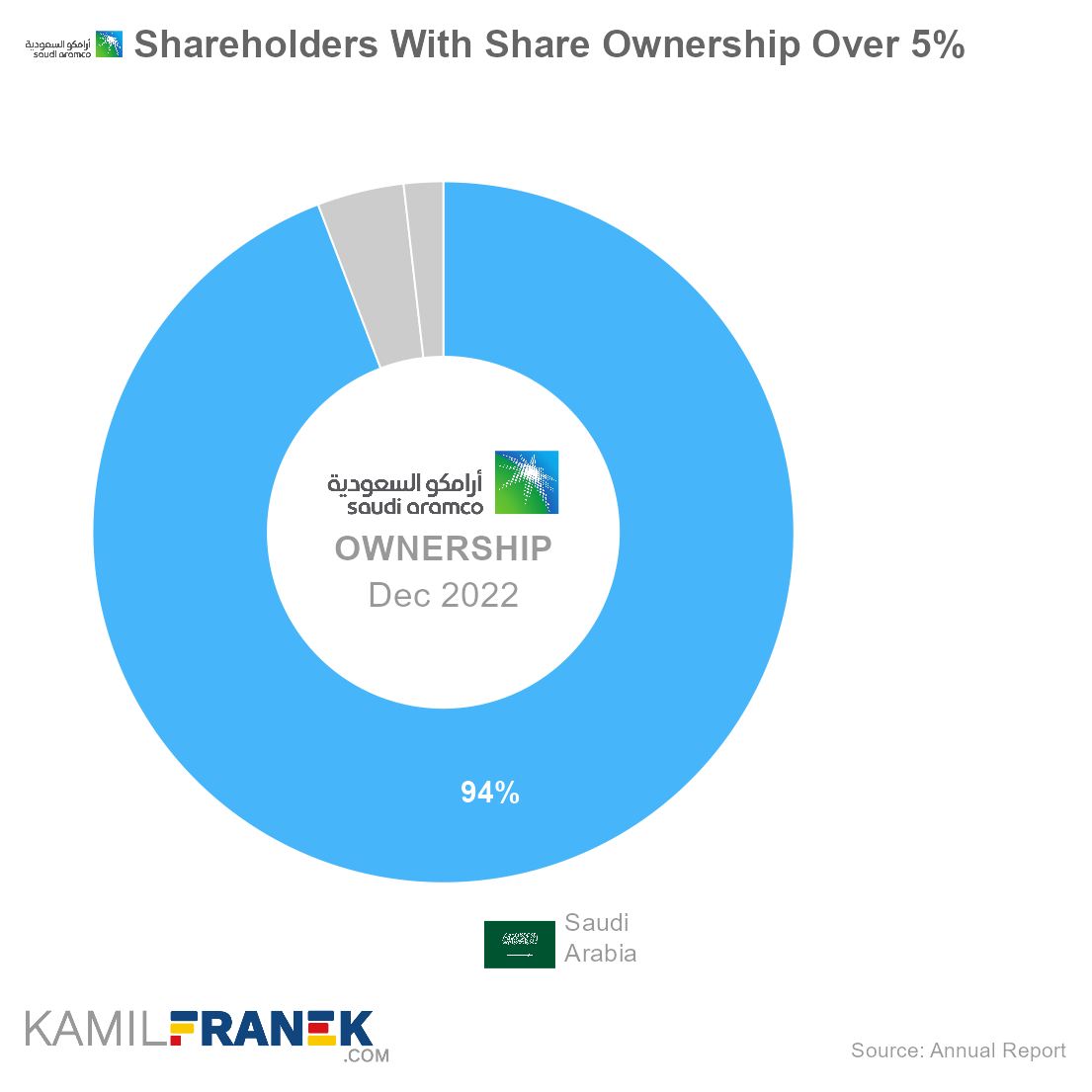
Saudi Aramco is predominantly owned by the Saudi Arabia government, which owns 98.2% of the company. Most of it is held directly by the government, and a 4.0% ownership share is held by Saudi Arabia’s sovereign wealth fund PIF.
The largest owner of Saudi Aramco is Saudi Arabia, which owns 94.2% of the company.
- Since 1980, Aramco has been 100% owned by Saudi Government. It is only since 1999 that Saudi Arabia floated a tiny part of it on their stock exchange.
- Only 1.73% of Saudi Aramco was sold during the IPO
The second-largest Saudi Aramco owner is PIF (Saudi Arabia), Saudi’s sovereign wealth fund, which owns a 4.0% stake.
- Public Investment Fund (PIF) is Saudi Arabia’s sovereign wealth fund, so again, its share is also in the hand of the Saudi government.
- Saudi Arabia transferred 4% of its stake in Saudi Aramco to PIF only in 2022
Saudi Aramco was founded in 1934 by Standard Oil Company of California (later Chevron) and has been a publicly listed company since its initial public offering on Tadawul (Saudi Exchange) in 2019 (Ticker: SR:2222).
- The story of the founding of Saudi Aramco is quite interesting. Today Aramco is a government-owned company, but if you look at its origins in the 1930s and 1940s, you will realize that Aramco was in the hands of US oil companies.
- Initially, the company was 100% owned by Standard Oil of California (today Chevron). Later it was 50% Chevron and 50% Texaco.
- In 1948, stakes were held by Standard Oil of California (later Chevron) (30%), Texas Company (later Texaco) (30%), Standard Oio of New Jersey (later Exxon) (30%), and Socony Vacuum (later Mobil) (10%).
Saudi Arabian Oil Company is incorporated in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and its headquarters are in Dhahran (Saudi Arabia).
🎮 Who Controls Saudi Aramco (SR:2222)?
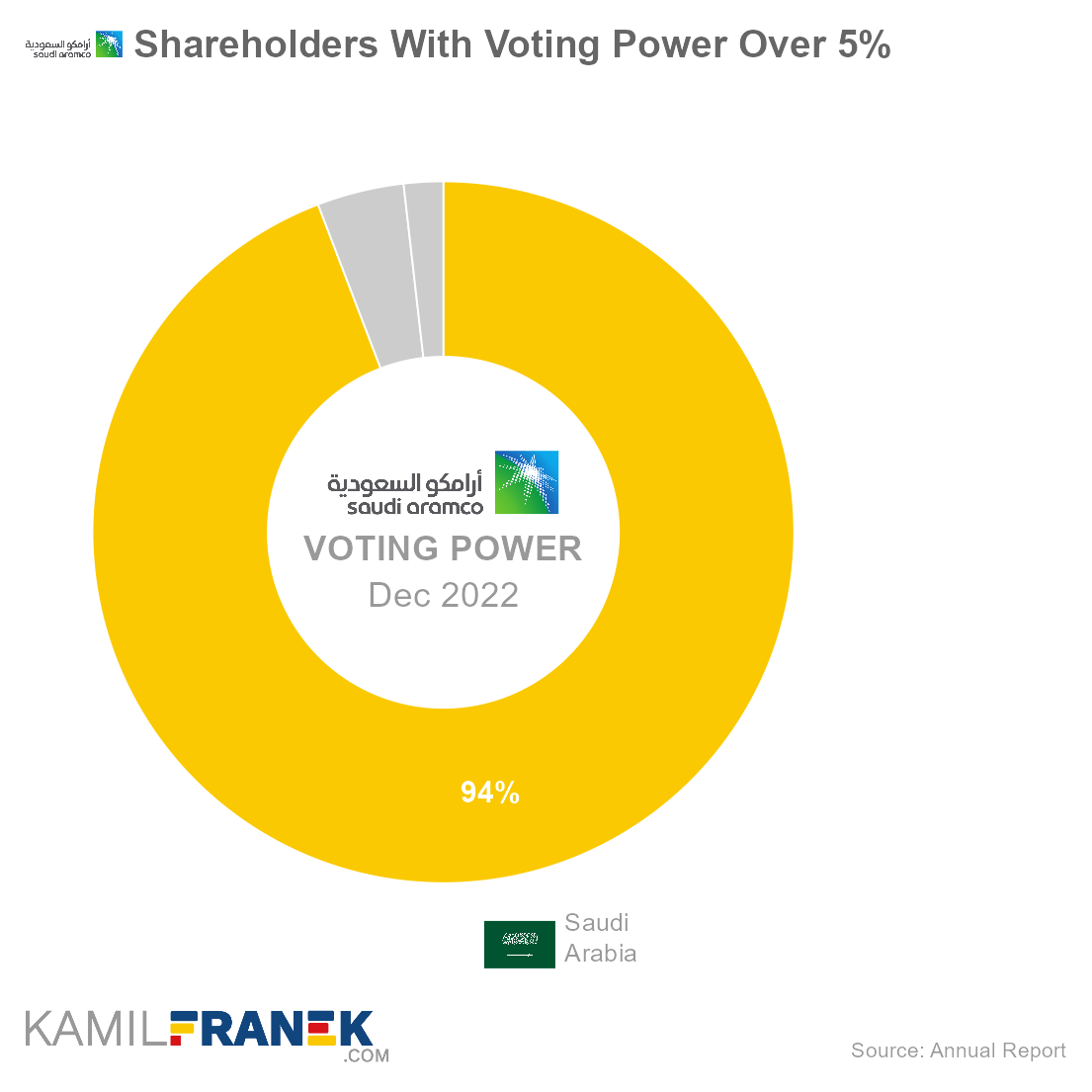
Saudi Aramco is predominantly controlled by the Saudi Arabia government. Saudi Arabia controls 94.2% of voting power directly and another 4.0% through its Public Investment Fund (PIF). But it does not stop there, and government influence goes much further.
Saudi Aramco has only one class of outstanding shares, with one vote per share. Therefore, there is no difference between the shareholder’s ownership and voting power.
However, as I mentioned, government control in Saudi Aramco goes beyond standard majority ownership. For example, the Saudi government can set the maximum oil production level at any time.
And the unfortunate fact for non-government shareholders is that even laws can be changed if needed.
Saudi Aramco’s insiders that have influence over the company are CEO Amin H. Nasser, chairman of the board Yasir Othman Al-Rumayyan, and other board members and executives.. However, since the government fully controls the company, the government, or more precisely, Saudi Arabia’s king and crown prince, are in charge.
- Saudi Aramco currently has an 11-member board of directors.
- Any shareholder holding at least 0.1% of the company can nominate a candidate, but with such voting power, nobody gets elected without the government’s support
- President and CEO are automatically a member of the Board without a need to be elected. They are nominated by the Board of Directors.
- The chairman and deputy chairman are specifically appointed by the Saudi Arabia state, not the shareholders. Although currently, this is an irrelevant distinction.
- The chairman cannot be an executive.
🗳️ Breakdown of Saudi Aramco’s Outstanding Shares and Votes by Top Shareholders
Saudi Arabian Oil Company had a total of 219,923 million outstanding shares as of December 2022. The following table shows how many shares each Saudi Aramco’s large shareholder holds.
|
|
||||
| In millions of shares as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 207,146 | 207,146 | 94.2% | |
| PIF (Saudi Arabia) | 8,797 | 8,797 | 4.0% | |
| Other | 3,981 | 3,981 | 1.8% | |
| Total (# millions) | 219,923 | 219,923 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Annual Report Source: Annual Report |
||||
There were 219,923 million votes distributed among shareholders of Saudi Arabian Oil Company. The table below shows the total number of votes for each large shareholder.
|
|
||||
| In millions of votes as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 207,146 | 207,146 | 94.2% | |
| PIF (Saudi Arabia) | 8,797 | 8,797 | 4.0% | |
| Other | 3,981 | 3,981 | 1.8% | |
| Total (# millions) | 219,923 | 219,923 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Annual Report Source: Annual Report |
||||
💵 Breakdown of Saudi Aramco’s Market Value by Shareholder
The following table summarizes how much is each shareholder’s stake in Saudi Arabian Oil Company worth.
However, keep in mind that a stake in Saudi Aramco could be just one part of their portfolio, and their total worth could be bigger, thanks to other investments. It could also be lower if they have debts.
|
|
||||
| Market value in billions $ as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | $1,771 | $1,771 | 94.2% | |
| PIF (Saudi Arabia) | $75 | $75 | 4.0% | |
| Other | $34 | $34 | 1.8% | |
| Total ($ billions) | $1,880 | $1,880 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Annual Report Source: Annual Report |
||||
Let’s now look at each Saudi Aramco shareholder individually.
📒 Who Are Saudi Aramco’s Largest Shareholders?
Let’s now go through the list of the largest shareholders of Saudi Arabian Oil Company one by one and look at who they are, how many shares they own, what is their voting power, and how much is their stake in Saudi Aramco worth.
#1 Saudi Arabia (94.2%)
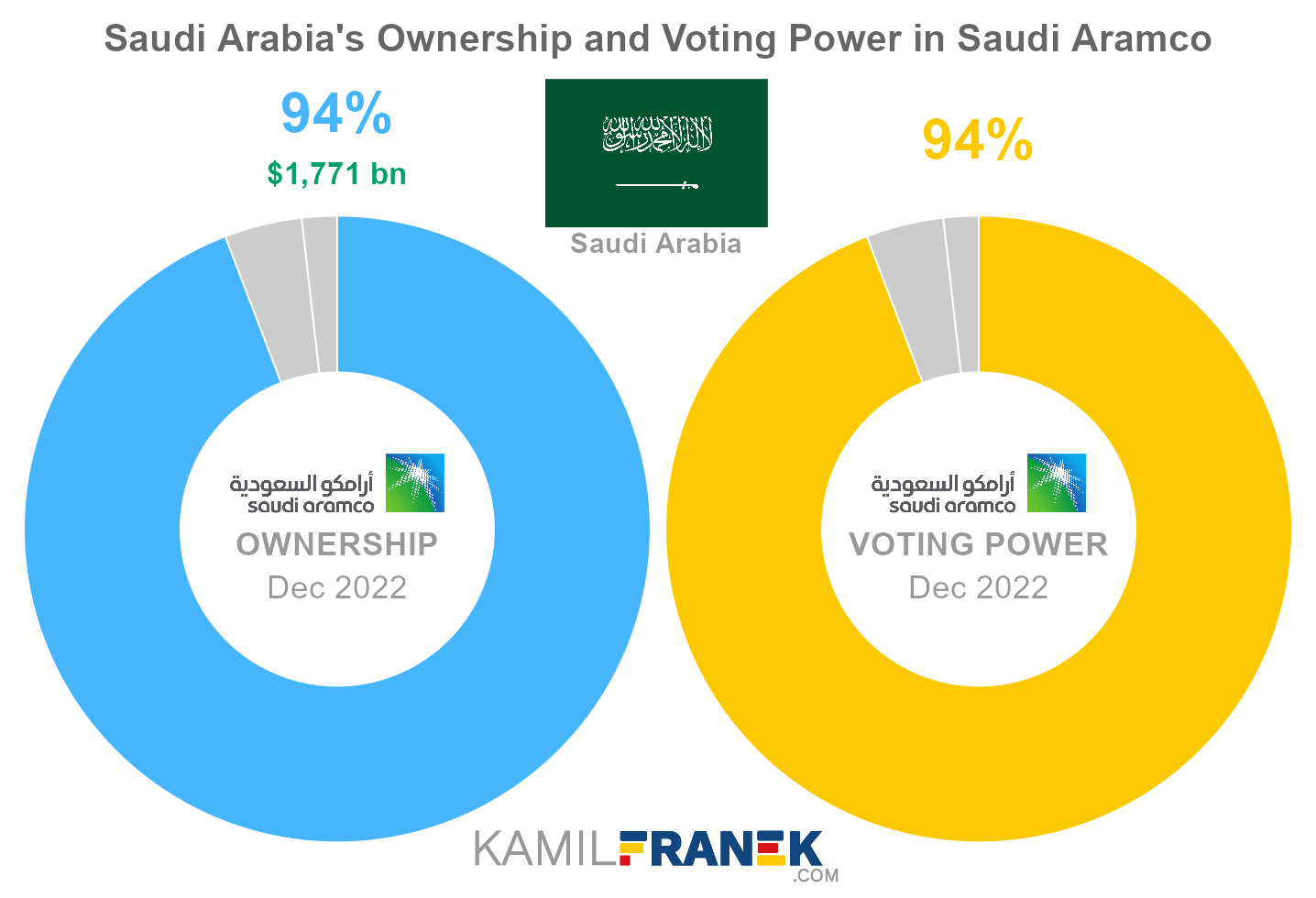
Saudi Arabia is the largest shareholder of Saudi Aramco, owning 94.2% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of Saudi Arabia’s stake in Saudi Aramco was $1,770.7 billion.
Saudi Arabia owned 207,146 million shares in Saudi Aramco and controlled 207,146 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
Saudi Arabia is a country rich in history, culture, and especially oil and sand. Saudi Arabia is a monarchy ruled by the Al Saud royal family.
The head of state is King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, supported by the Council of Ministers. The council of ministers is headed by prime minister, which is currently the king’s son Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud (MBS).
MBS is considered to be the ruler of Saudi Arabia as he is also the crown prince and official successor of his father, the king of Saudi Arabia.
#2 PIF (Saudi Arabia) (4.0%)
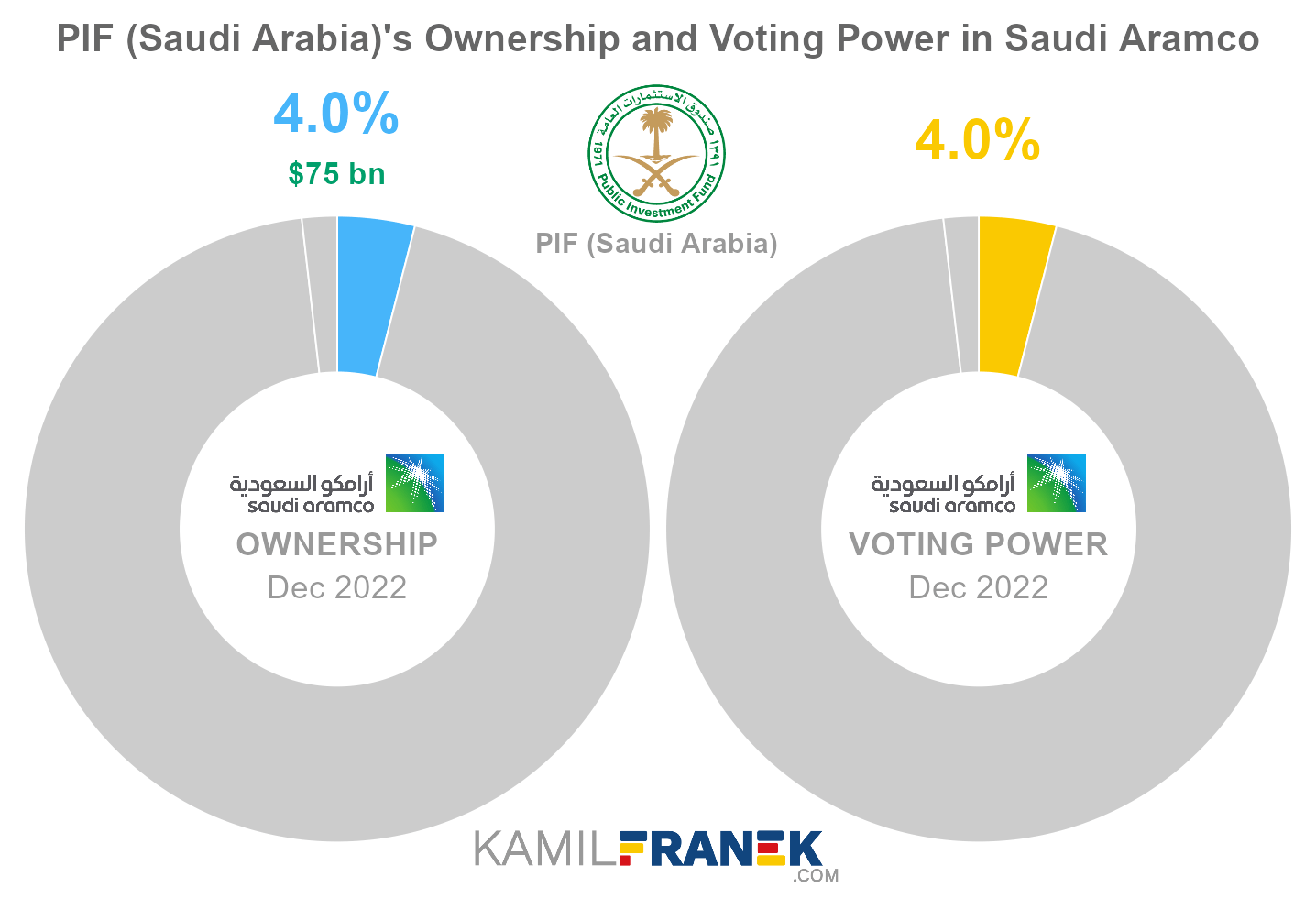
PIF (Saudi Arabia) is the second-largest shareholder of Saudi Aramco, owning 4.0% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of PIF (Saudi Arabia)’s stake in Saudi Aramco was $75.2 billion.
PIF (Saudi Arabia) owned 8,797 million shares in Saudi Aramco and controlled 8,797 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
Public Investment Fund (PIF) is the sovereign wealth fund of Saudi Arabia. It was established in 1971 to diversify Saudi Arabia’s economy. It is one of the largest sovereign funds in the world, having a stake in many Western companies. The fund is governed by its board, headed by nobody else than Saudi Arabia’s crown prince Mohammad bin Salman Al-Saud (MBS).
🧱 Who and When Founded Saudi Aramco?
Saudi Aramco was founded in 1934 by Standard Oil of California (now known as Chevron) to explore and pump oil in Saudi Arabia. It was initially named California-Arabian Standard Oil (CASOC) and was later renamed Arabian American Oil Co. (ARAMCO).
Saudi Aramco (Saudi Arabian Oil Company) is now predominantly owned by the Saudi government. However, it was initially founded by the US oil company “Standard Oil of California,” a company that is today known as Chevron. It was only later that Aramco transformed into the wholly-owned state oil giant as we know it today.
In 1933, the Saudi Arabian government granted a concession to Standard Oil Co. of California to explore oil in the country. The company struck oil in Bahrain just a few years ago.
Standard Oil Co. of California transferred this concession to its wholly owned subsidiary called California-Arabian Standard Oil (CASOC) in 1934 and started looking for oil.
After a few years of exploration with no success, another US company, “Texas Company” (later renamed Texaco), purchased a 50% stake in CASOC in 1936.
However, it took another few years until March 1938 when the well “Damman No.7” struck oil, and the largest source of crude oil in the world was revealed.
In 1944, the company was renamed from California-Arabian Standard Oil Co. (CASOC) to Arabian American Oil Co. (ARAMCO).
In 1948, Standard Oil of New Jersey (later Exxon) purchased 30% of ARAMCO, and Socony Vacuum (later Mobil) purchased 10%. Standard Oil of California (later Chevron) and Texaco retained 30% each.
As the fat profits flew into US oil companies’ pockets and only a fraction of it was paid as royalties to the Saudi government, King Abd al-Aziz threatened to nationalize the company.
This led to negotiations, and in 1950 a 50:50 profit-sharing agreement was signed, significantly increasing Saudi Arabia’s revenues.
Later, during the 1970s, Saudi Arabian gained 100% interest in ARAMCO. Initially, it acquired 25% in 1973, increased it to 60% in 1974, and then finally gained 100% in 1980.
In 1988, ARAMCO was transformed into the Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco), the company we today know as ARAMCO.
📅 Saudi Aramco’s History Timeline
These are selected events from Saudi Aramco’s history:
-
1933: The Saudi Arabian government granted a concession to Standard Oil Co. of California (later known as Chevron) to explore oil. Standard Oil of California had recently struck oil in Bahrain.
-
1934: Standard Oil of California assigned the concession to a wholly owned subsidiary, California-Arabian Standard Oil (CASOC).
-
1935: Drilling begins in the Saudi desert for oil.
-
1936: Texas Company (later Texaco) purchased a 50% stake in California-Arabian Standard Oil after no success at locating oil.
-
1938 (March): Dammam No. 7 strikes oil and reveals the largest source of crude oil in the world
-
1938: The company began primary drilling operations shortly after the agreement, commencing its first commercial oil production.
-
1939: First tanker load of petroleum exported
-
1940: Abqaiq field discovered
-
1944 The company name was changed from California-Arabian Standard Oil Co.(CASOC) to Arabian American Oil Co. (ARAMCO)
-
1948: Standard Oil of New Jersey (later known as Exxon) purchased 30% of ARAMCO, and Socony Vacuum (later Mobil) purchased 10% of the company. Standard Oil of California (later Chevron) and Texaco retained 30% each.
-
1949: Crude oil production hits 500,000 barrels per day.
-
1949: ARAMCO agrees to a greater area to search for oil and extends the concession until 1949, increasing the original deal by six years
-
1950: After the realization that only a fraction of Aramco’s profits flows as royalties to the Saudi government, King Abd al-Aziz threatened to nationalize his country’s oil facilities, thus pressuring Aramco to agree to share more profits.
-
1950: ARAMCO and the Saudi Arabian government signed a fifty-fifty profit-sharing agreement, increasing government revenues.
-
1951: The company discovered the Safaniya Oil Field, the world’s largest offshore field
-
1952: Headquarters moved from New York City to Dhahran
-
1958: Aramco’s crude oil production exceeded 1 million barrels in a calendar year
-
1965: Zafer H. Husseini was named the first Saudi manager
-
1973: Saudi government bought a 25% interest in Aramco
-
1973: The Yom Kippur War causes the price of oil to increase drastically, allowing Saudi Arabia to gain much wealth and power
-
1974: The Saudi Arabian government increased its participation interest to 60%.
-
1974: Faisal Al-Bassam was named the first Saudi vice president
-
1976: Production of more than 3 billion barrels of oil in a year
-
1980: The government of Saudi Arabia increased its interest in ARAMCO to 100%.
-
1984: Ali I. Al-Naimi appointed the company’s first Saudi president
-
1988: Aramco was transformed into the Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco).
-
1988: Al-Naimi became CEO, and Hisham Nazer became chairman, the first Saudis to hold both positions
-
1989: Aramco formed a joint venture with Texaco in the US called Star Enterprises.
-
1993: Saudi government issued a royal decree merging Saudi Aramco with Samarec (Saudi Arabian Marketing and Refining Company)
-
2003: Royal Dutch Shell and Total partnered with Saudi Aramco to find and pump oil, becoming the first Western oil companies in decades to do that.
-
2003: Other partnerships of Aramco with other foreign companies signed.
-
2009: Petro Rabigh, Aramco’s first petrochemical plant, begins production
-
2011: Sadara Chemical Company joint venture formed with Dow Chemical.
-
2016: Mohammed bin Salman bin Abdulaziz Al-Saud announced plans to list 5% at a valuation of approximately $2 trillion in what became the largest IPO.
-
2017: Saudi Aramco became the sole owner of North America’s largest single-site crude oil refinery at Port Arthur, Texas.
-
2019 Drone attack on two Saudi Aramco plants. Houthi rebels claimed responsibility for the attack. The attack cut over 5% of the world’s supply.
-
2019: Saudi Arabia appointed Yasir Al-Rumayyan as the Chairman of Aramco
-
2019: Aramco becomes a public company with shares listed on Tadawul. Even after the IPO, Saudi Government retains over 98% ownership of Aramco.
-
2020: Saudi Aramco acquired a 70% share in SABIC, a chemicals manufacturing company.
-
2023: Saudi Aramco announced record profits of $161 billion as prices of petrol soared following the Coronavirus pandemic.
📚 Recommended Articles & Other Resources
Who Owns Tesla: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Tesla and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Exxon Mobil: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Exxon Mobil and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Netflix: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Netflix and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns L’Oréal: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns L’Oréal and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Lenovo: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Visual overview of who owns Lenovo and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Lockheed Martin: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Lockheed Martin and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth..
Other Resources
Disclaimer: Although I use third-party trademarks and logos in this article and its visuals, kamilfranek.com is an independent site, and there is no relationship, sponsorship, or endorsement between this site and the owners of those trademarks.

