Who Owns JPMorgan Chase: The Largest Shareholders Overview

JPMorgan Chase & Co. (JPM) is the largest US bank that is active mainly in consumer & small business banking and investment banking and, to a lesser extent, also in commercial banking and asset management. Let’s look at who owns JPMorgan Chase and who controls it.
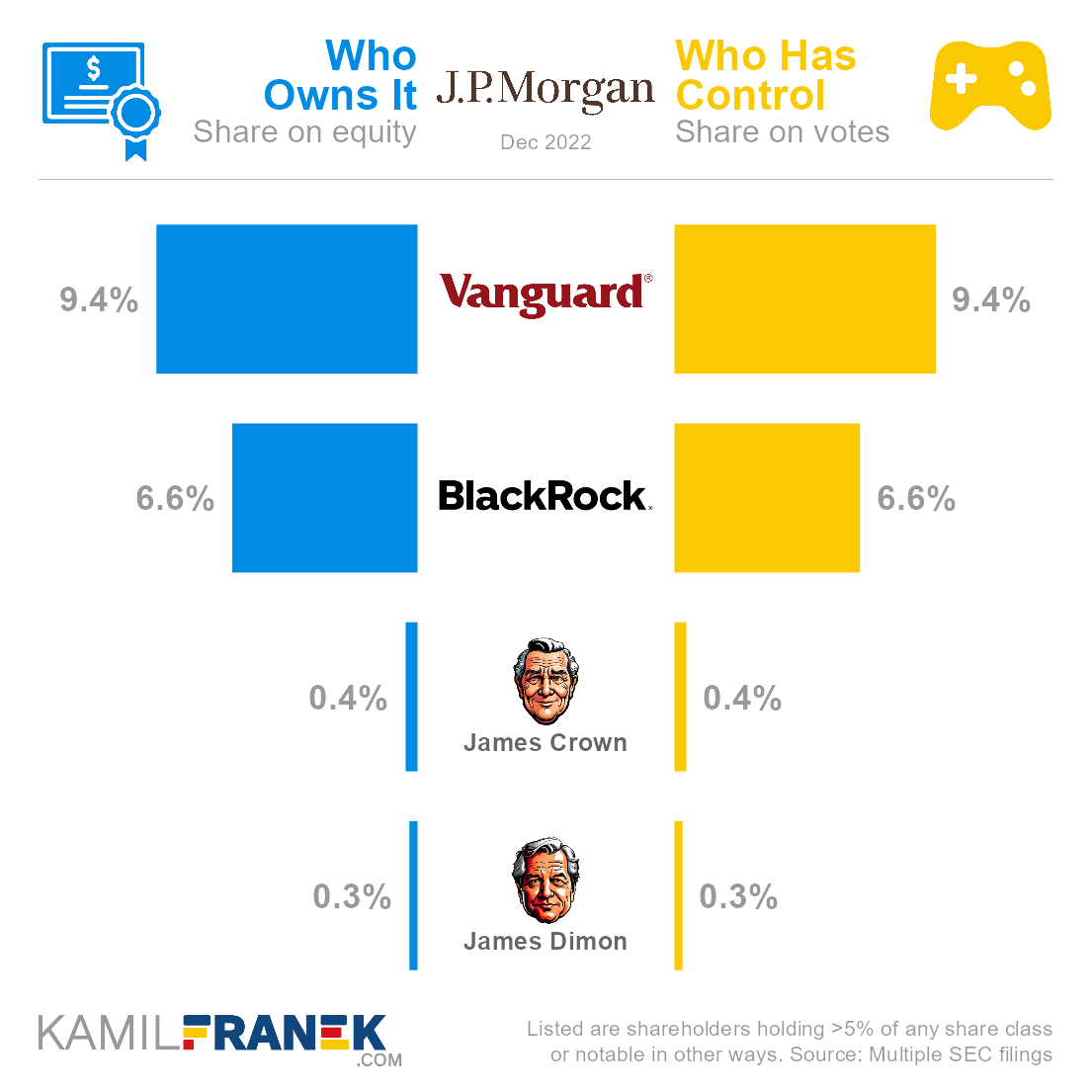
JPMorgan Chase’s largest shareholders are asset manager giant Vanguard, which owns a 9.4% share, followed by asset manager giant BlackRock with a 6.6% ownership share. Sizable stakes also belong to James Crown (0.4%) and JPMorgan Chase’s CEO & chairman James Dimon (0.3%).
|
|
|||
| Shareholder | Ownership | Voting Power | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard | 9.4% | 9.4% | |
| BlackRock | 6.6% | 6.6% | |
| James Crown | 0.4% | 0.4% | |
| James Dimon | 0.3% | 0.3% | |
| Other | 83.3% | 83.3% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | |||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
|||
In this article, I will dive more into who owns JPMorgan Chase and who controls it. I will show you who JPMorgan Chase’s largest shareholders are, how many shares and votes they have, and how much their stake is worth.
If you are interested, you can also explore who owns other companies like Visa, Apple, PayPal, and other articles in my “Who Owns Who” series.
📃 Who Owns JPMorgan Chase?
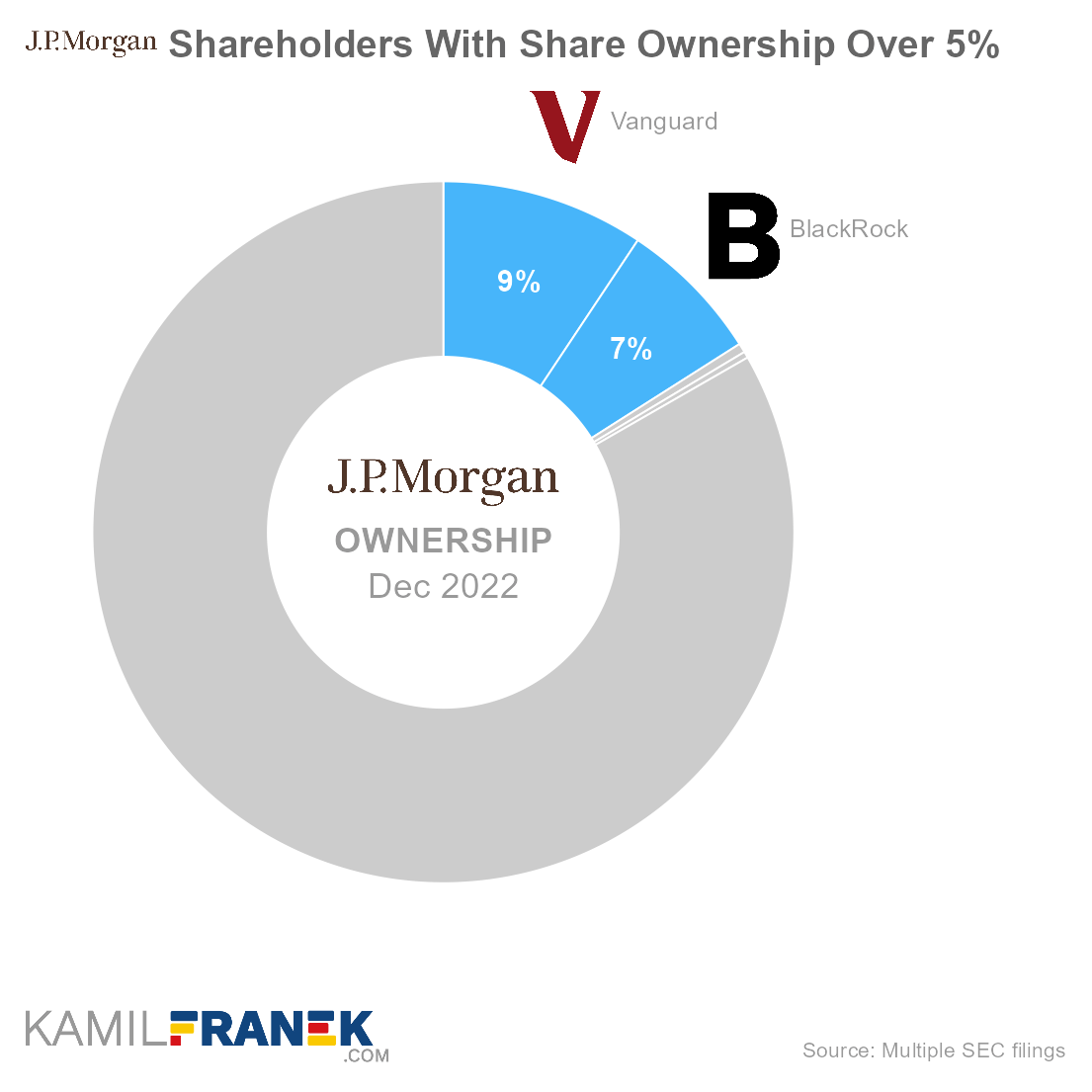
JPMorgan Chase is owned mainly by asset manager giant Vanguard, which owns 9.4% of the company, and asset manager giant BlackRock with a 6.6% ownership share. Notable owners are also board director James Crown with 0.4% ownership share, and JPMorgan Chase’s CEO James Dimon with 0.3% ownership.
No shareholder has dominant ownership in the company.
- JPMorgan Chase’s ownership is dispersed, and the largest owners are asset managers who invest money on behalf of their clients.
The asset manager giants Vanguard and BlackRock own together 16.0% of the company.
- Vanguard and BlackRock are the largest asset managers worldwide, and it is common to see them among top shareholders in large public companies with dispersed ownership.
Notable owner is also the Crown family, represented by JPMorgan Chase’s director James Crown, with a 0.4% stake.
- His stake represents the ownership of the whole influential Chicago-based Crown family. The Crown family belongs to the wealthiest families in the US.
- Crown family ownership is held through various entities. The largest stake is owned by “The Crown Fund” and “HCNI II LLC.”
- James Crown was originally on the board of Bank One and moved to the JPMorgan Chase board after Jamie Dimon engineered the sale of Bank One to JPMorgan in 2004. James Crown supposedly played an instrumental role in recruiting Jamie Dimon to Chicago in 2000 to become CEO of Bank One Corp.
Another notable owner is also CEO & Chairman James Dimon. He sometimes acts as if he owns the bank, but his ownership is “only” 0.3% of the company.
- Although Jamie Dimon’s ownership is small, it is quite high for a public company CEO. His dividend income from the shares he owns is roughly equal to his annual compensation as company CEO and chairman.
- He owns only a small portion of his stake directly. Most of it is owned through his Family Trust and Grantor Retained Annuity Trust.
- Jamie Dimon and James Crown’s relationship goes way back, as James Crown is often cited as a man who persuaded Jamie Dimon to join Bank One.
Warren Buffett’s company Berkshire Hathaway had a sizable stake in JPMorgan Chase but got rid of most of its position in the first half of 2020.
JPMorgan Chase is a result of multiple mergers, and the earliest company in the chain is The “Bank” of the Manhattan Company, co-founded in 1799 by Aaron Burr, the man who killed Alexander Hamilton. The company is publicly listed on NYSE (Ticker: JPM).
- The company is a result of chains of multiple mergers and acquisitions. The core building blocks are:
- The Bank of the Manhattan Company founded in 1799
- Chase National Bank founded in 1877
- J.P. Morgan & Co. founded in 1871
- Initially, The Bank of the Manhattan Company merged with Chase National Bank in 1955. Later in 2000, resulting Chase Manhattan Bank merged with J.P. Morgan & Co., creating JPMorgan Chase & Co.
- Bank later gobbled up other competitors during the 2008 financial crises.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is incorporated in the State of Delaware (US), and its headquarters are in New York City (US).
🎮 Who Controls JPMorgan Chase (JPM)?
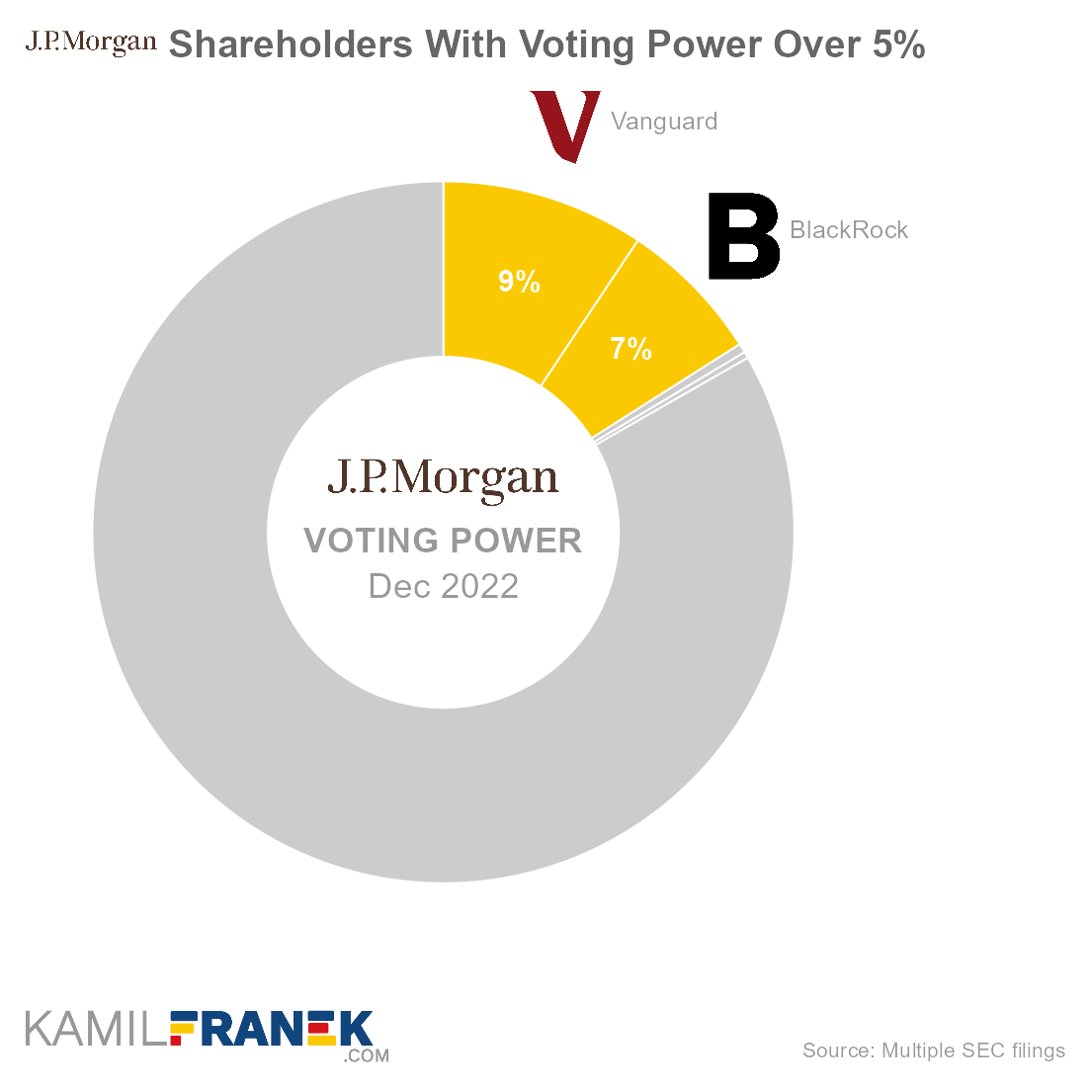
JPMorgan Chase’s shareholders with the largest voting power are Vanguard, which holds 9.4% of all votes, followed by asset manager giant BlackRock (6.6%). However, real control over the company is exercised by its CEO, James Dimon, thanks to his influence and political clout.
The size of voting power is not fully equal to ownership because of the small amount of non-voting preferred shares that JPMorgan Chase has outstanding. However, the amount of preferred shares is so small that this difference is not material.
The ownership of JPMorgan Chase & Co. is quite dispersed, and the main shareholders are asset managers investing money on behalf of their clients. None of them control the company individually, but together they have a big potential influence.
In situations like these, insiders of the large asset manager shareholders and insiders of the company could gain significant power over it, and that is what happened in JPMorgan Chase.
In the case of JPMorgan Chase, this shareholder power vacuum is masterfully used by current CEO and chairman Jamie Dimon. He holds just 0.3% of all votes, which is a sizable amount for a CEO, but not enough to formally control the company. However, in the absence of other large shareholders that are not asset managers, his ownership stake doesn’t matter so much.
- He is very well-skilled in playing this game. With the help of his reputation, connections, political clout, and company board stacked with his supporters, he clearly has outsized power over the company.
- Jamie Dimon has the support of the Crown family, which holds 0.4% of all votes. The family is represented by James Crown, who reportedly played an important role in recruiting Jamie Dimon to Chicago in 2000 to become CEO of Bank One Corp. The Crown family was a shareholder of Bank One, which later merged with JPMorgan Chase, and James Crown became the director.
- Mr. Dimon had a very good relationship with Obama’s White House, and at the time, President Obama even defended him publicly on TV. Just another testament to Jamie Dimon’s influence.
JPMorgan Chase’s insiders that have influence over the company are mainly CEO and chairman Jamie Dimon and other board members and executives.
- JPMorgan Chase’s board of directors consists of 11 members who are reelected annually.
- As I mentioned earlier, the company board is quite supportive of Mr. Dimon, and several board members have a joint history with him. One of them is James Crown.
- Another board member with a connection to Mr. Dimon is Linda Bammann, who worked under Jamie Dimon when he was at Bank One. This issue was raised and discussed by shareholders when she was first proposed to become a director in 2013. The result was that the shareholder lost, and Mr. Dimon won. Another testament to how much heft he holds over the company.
- Another notable board member is Todd Combs from Berkshire Hathaway, despite Berkshire exiting its position it had in JPMorgan Chase a few years ago.
- On the other hand, unlike other public company CEOs, Mr. Dimon’s interests are pretty well aligned with that of the company since he owns a sizable stake in the company compared to his annual compensation.
- Shareholders benefited from several backdoor deals that Mr. Dimon managed to do with the government and regulators, helping JPMorgan Chase to grow its assets cheaply by acquiring other banks in distress with government help.
🗳️ Breakdown of JPMorgan Chase’s Outstanding Shares and Votes by Top Shareholders
JPMorgan Chase & Co. had a total of 2,937 million outstanding shares as of December 2022. The following table shows how many shares each JPMorgan Chase’s large shareholder holds.
|
|
|||||
| In millions of shares as of December 2022 | |||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Class P | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard | 275 | - | 275 | 9.4% | |
| BlackRock | 195 | - | 195 | 6.6% | |
| James Crown | 12 | - | 12 | 0.4% | |
| James Dimon | 8 | - | 8 | 0.3% | |
| Other | 2,444 | 3 | 2,446 | 83.3% | |
| Total (# millions) | 2,934 | 3 | 2,937 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | |||||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
|||||
There were 2,934 million votes distributed among shareholders of JPMorgan Chase & Co.. The table below shows the total number of votes for each large shareholder.
|
|
||||
| In millions of votes as of December 2022 | ||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard | 275 | 275 | 9.4% | |
| BlackRock | 195 | 195 | 6.6% | |
| James Crown | 12 | 12 | 0.4% | |
| James Dimon | 8 | 8 | 0.3% | |
| Other | 2,444 | 2,444 | 83.3% | |
| Total (# millions) | 2,934 | 2,934 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | ||||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
||||
💵 Breakdown of JPMorgan Chase’s Market Value by Shareholder
The following table summarizes how much is each shareholder’s stake in JPMorgan Chase & Co. worth.
However, keep in mind that a stake in JPMorgan Chase could be just one part of their portfolio, and their total worth could be bigger, thanks to other investments. It could also be lower if they have debts.
|
|
|||||
| Market value in billions $ as of December 2022 | |||||
| Shareholder | Class A | Class P | Total | % Share | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard | $36.8 | - | $36.8 | 9.4% | |
| BlackRock | $26.1 | - | $26.1 | 6.6% | |
| James Crown | $1.7 | - | $1.7 | 0.4% | |
| James Dimon | $1.1 | - | $1.1 | 0.3% | |
| Other | $327.7 | $0.4 | $328.1 | 83.3% | |
| Total ($ billions) | $393.5 | $0.4 | $393.8 | 100.0% | |
| Listed are shareholders holding >5% of any share class or notable in other ways | |||||
 Source: Multiple SEC filings Source: Multiple SEC filings |
|||||
Let’s now look at each JPMorgan Chase shareholder individually.
📒 Who Are JPMorgan Chase’s Largest Shareholders?
Let’s now go through the list of the largest shareholders of JPMorgan Chase & Co. one by one and look at who they are, how many shares they own, what is their voting power, and how much is their stake in JPMorgan Chase worth.
#1 Vanguard (9.4%)
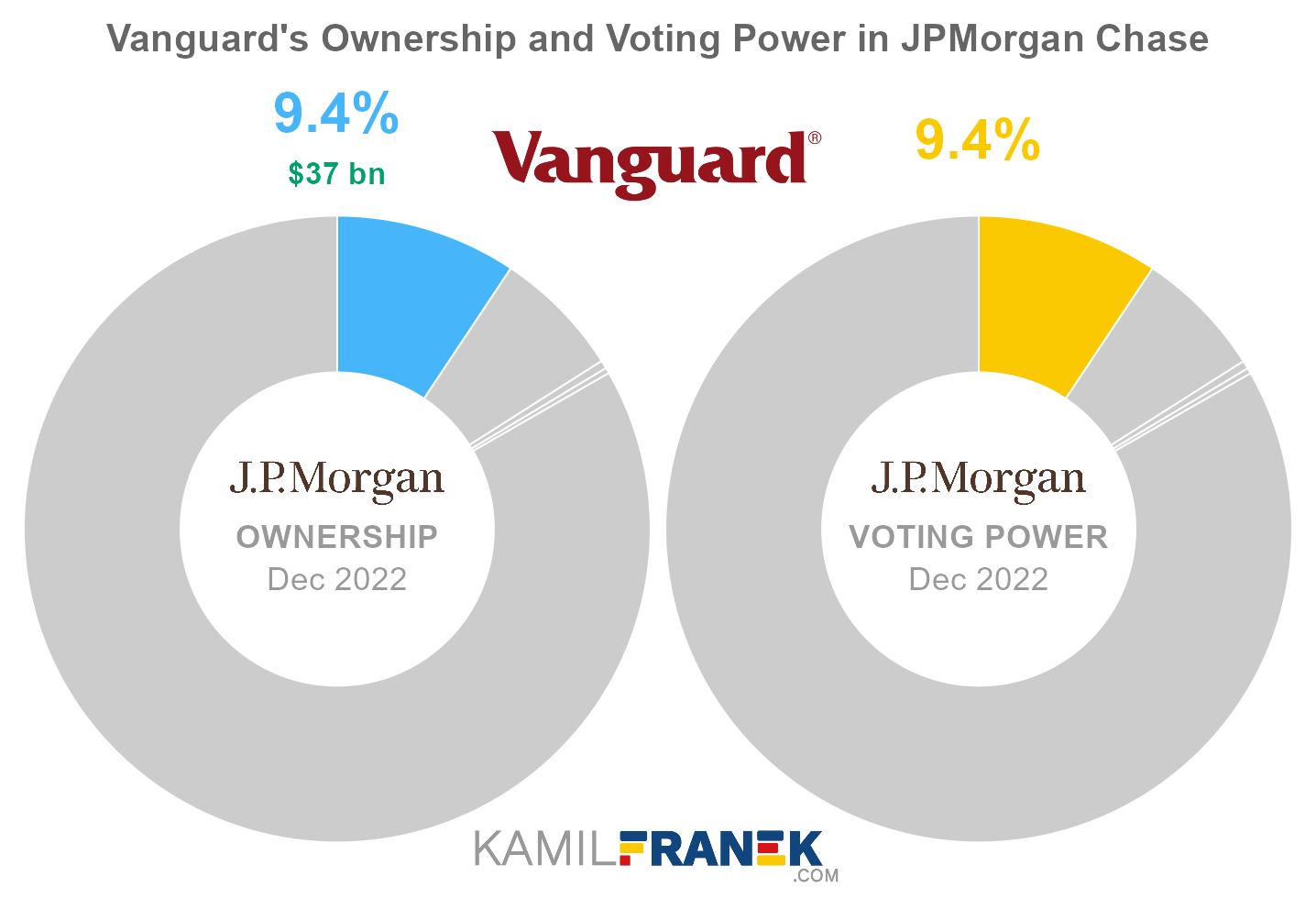
Vanguard is the largest shareholder of JPMorgan Chase, owning 9.4% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of Vanguard’s stake in JPMorgan Chase was $36.8 billion.
Vanguard owned 275 million shares in JPMorgan Chase and controlled 275 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
Vanguard (The Vanguard Group) is one of the largest asset managers in the world. It manages other people’s money through its mutual funds and exchange-traded funds and also offers other related investing and financial planning services.
Vanguard differs from other large asset managers by having no actual “owner .” Officially Vanguard says that its investors own it since its funds own it, and Vanguard fund investors own those funds.
However, the actual decision power is in the hands of Vanguard’s insiders since the ownership is diluted over millions of investors worldwide.
Vanguard has significant influence over the largest public companies. Thanks to its size, Vanguard usually belongs to the largest shareholders in those companies and has considerable power at their shareholder meetings. This is especially true if ownership is diluted.
- Several terms were coined to describe this issue. Some call it asset manager capitalism, and popular is also the power of twelve. Financial Times even put together who exactly those twelve people might be.
- Evidence shows that big asset managers usually vote together with management.
#2 BlackRock (6.6%)
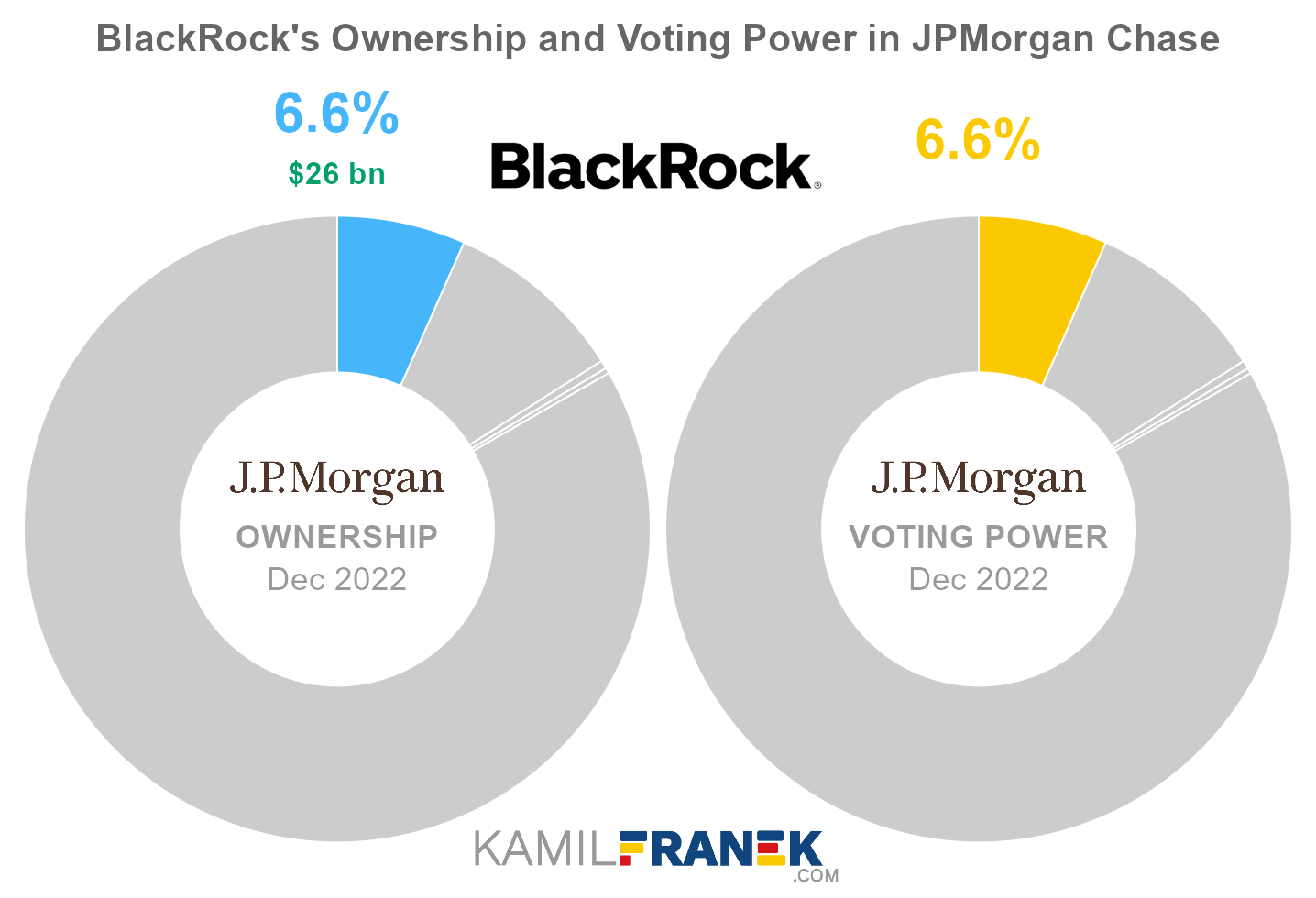
BlackRock is the second-largest shareholder of JPMorgan Chase, owning 6.6% of its shares. As of December 2022, the market value of BlackRock’s stake in JPMorgan Chase was $26.1 billion.
BlackRock owned 195 million shares in JPMorgan Chase and controlled 195 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
BlackRock, Inc. is the world’s largest asset manager, with assets under management of $10 trillion. BlackRock is not only an asset manager, but it also provides other asset managers and corporations with its Aladdin portfolio management software.
BlackRock is a publicly traded company, and its largest shareholders are its competitors, including BlackRock itself. Not directly but through their passive and active funds. The largest shareholder is Vanguard.
A similar situation is also true in the opposite direction because BlackRock is a significant shareholder in many of its publicly traded competitors and other large institutions, making the whole thing even more eyebrow-raising.
This circular ownership between Vanguard, BlackRock, and other large asset managers, amplifies the issue often raised about the power of these large asset managers over public companies since they usually belong to the most significant shareholders with large voting power.
-
In the case of Blackrock, this influence is personified in the form of its CEO Larry Fink, who is a powerful figure with close ties to the FED and the US government.
-
Adding to these concerns is evidence that BlackRock and other asset managers usually vote in favor of management proposals.
#3 James Crown (0.4%)
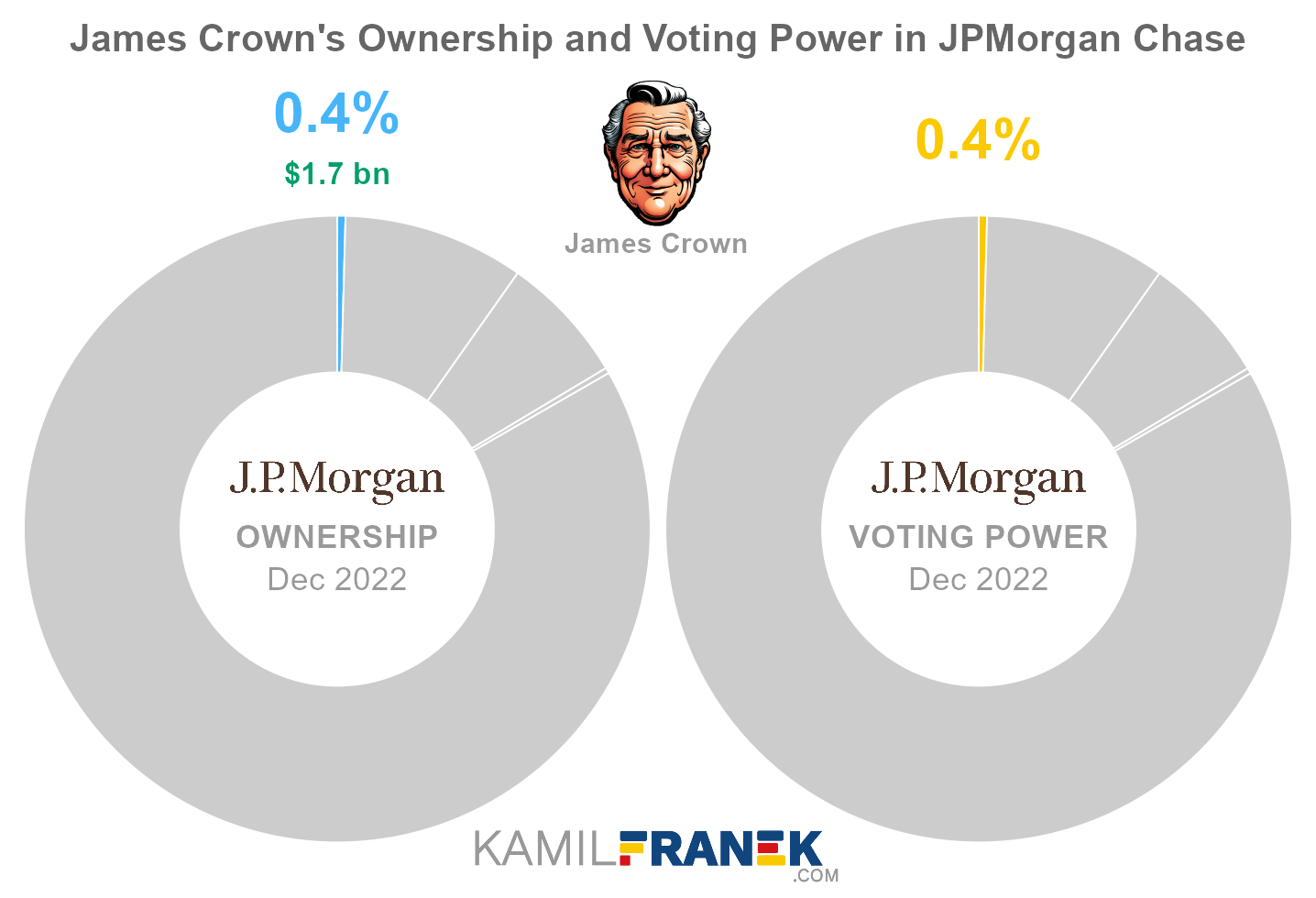
James Crown owns 0.4% of JPMorgan Chase’s shares. As of December 2022, the market value of James Crown’s stake in JPMorgan Chase was $1.7 billion.
James Crown owned 12 million shares in JPMorgan Chase and controlled 12 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
James Crown is a member of the wealthy Crown family and currently serves as the Chairman and CEO of the family’s investment firm, Henry Crown and Company. Alongside his leadership position in the family business, he also serves as a director at JPMorgan Chase and General Dynamics, both of which the Crown family has financial stakes in.
James Crown’s grandfather, Henry Crown, was a notable industrialist, and his father, Lester Crown, was a prominent business figure as well. The Crown family is considered one of the wealthiest families in the United States, and their investment firm owns a diverse range of business assets, including sports teams, leisure companies, banking institutions, and real estate holdings.
#4 James Dimon (0.3%)
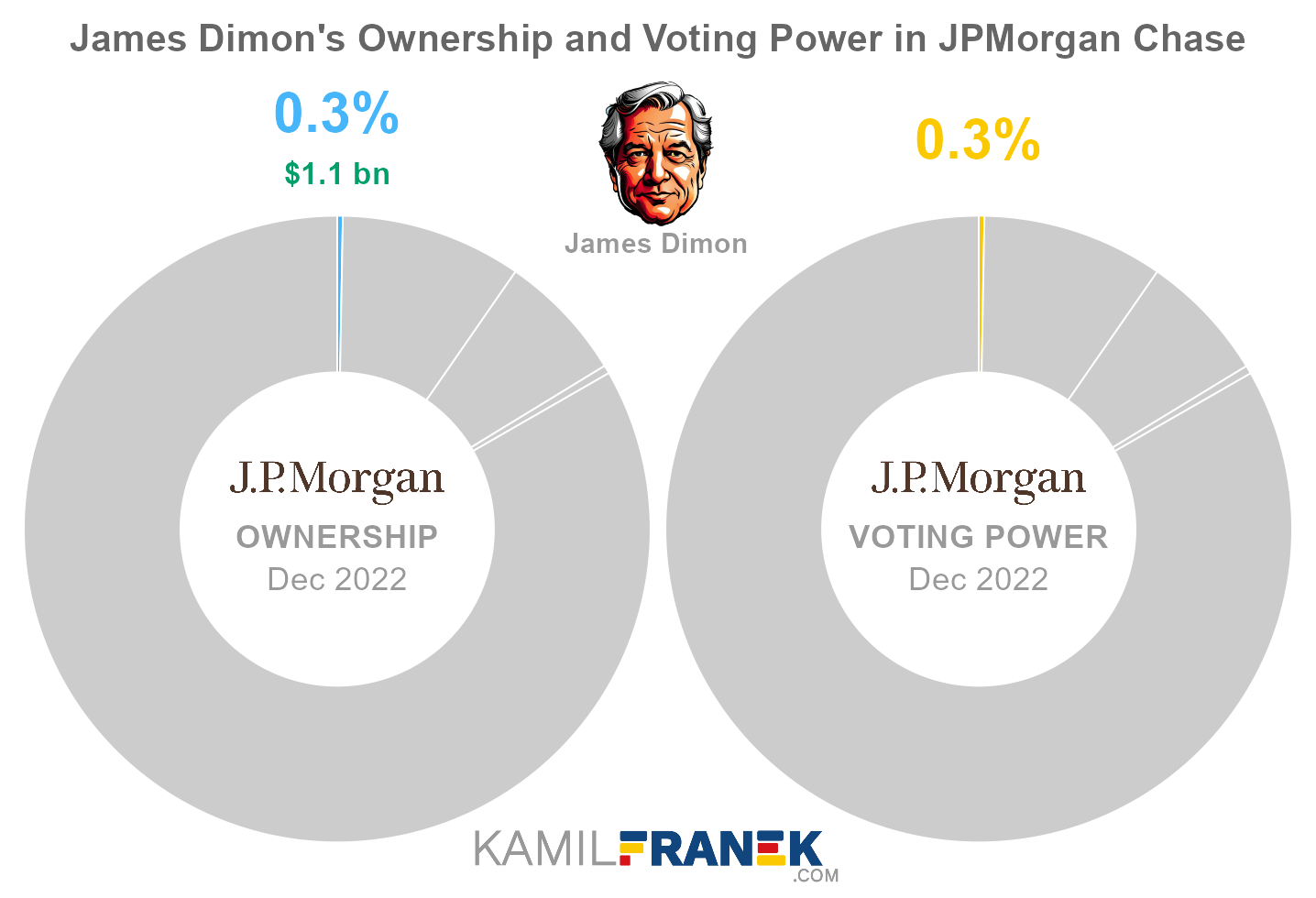
James Dimon owns 0.3% of JPMorgan Chase’s shares. As of December 2022, the market value of James Dimon’s stake in JPMorgan Chase was $1.1 billion.
James Dimon owned 8 million shares in JPMorgan Chase and controlled 8 million shareholder votes as of December 2022.
Jamie Dimon is the influential CEO and chairman of JPMorgan Chase, the largest bank in the United States. He is a very well-respected figure that commands immense power in the world of finance and politics. Despite several scandals at his bank during his tenure, he managed alwas to defend his his as the head of the company.
Before joining JPMorgan Chase, he was CEO of Chicago-based Bank One, which was acquired by JPMorgan Chase in 2004. Soon after that, he became CEO of the merged company.
Dimon’s political clout is evident in his frequent appearances before Congress, where he advocates for policies that benefit the banking industry.
🧱 Who and When Founded JPMorgan Chase?
Only a few companies have such a rich history as JP Morgan Chase & Co. Bank’s history spans to the time when the United States of America was founded, and its beginnings involve famous people of American history.
As you would expect, JP Morgan Chase’s history is full of interesting personalities, dodgy business dealings, and scandals. It was true when it was founded, and it continues to be true even today.
JPMorgan Chase is a result of multiple mergers and acquisitions. There were a lot of them, but the main steps were the merger of The Bank of the Manhattan Company and Chase National Bank in 1955. The combined bank was renamed Chase Manhattan Bank and, in 2000, merged with J.P. Morgan & Co, forming JPMorgan Chase.
Let’s look at who and when founded each of J.P. Morgan’s main predecessors one by one.
Who and When Founded the Bank of the Manhattan Company
In the late 18th century, New York City desperately needed clean drinking water. As a response, a group of businessmen and politicians decided to establish The Manhattan Company in 1799 to provide “pure and wholesome” drinking water to the people of New York.
Things did not go according to plan when it came to clean water, but within a few months, the company opened The Bank of The Manhattan Company, becoming the second commercial bank in New York City.
One of the bank’s founders was Aaron Burr, the man who killed Alexander Hamilton, one of the founders of the Bank of New York and former Secretary of the Treasury.
In 1804, Burr challenged Hamilton to a duel, resulting in Hamilton’s death. Burr was later charged with murder but was ultimately acquitted.
Despite its controversial beginnings, The Bank of The Manhattan Company thrived, and in 1955, it merged with Chase National Bank to form Chase Manhattan Bank.
Who and When Founded the Chase National Bank
Chase National Bank was founded by John Thompson in 1877. The bank was named after Salmon P. Chase, the Secretary of the Treasury under Abraham Lincoln and the National Banking System architect.
Many years later, in 1955, the bank merged with The Bank of The Manhattan Company to form Chase Manhattan Bank.
Who and When Founded J.P. Morgan & Co.
J.P. Morgan & Co. is one of the most renowned financial institutions in the world. The bank has a long history, dating back to 1864 when J. Pierpont Morgan founded his own firm in partnership with his cousin.
However, the roots of the Morgan banking family can be traced back to 1854, when his father, Junius S. Morgan, moved to London and joined George Peabody & Co., which became the leading marketer of American securities in England and Europe.
The official year of the founding of J.P. Morgan is considered 1871 when J. Pierpont Morgan partnered with Philadelphia banker Anthony Drexel to form Drexel, Morgan & Co., a private merchant banking house in New York City.
The new partnership allowed J. Pierpont Morgan to establish his reputation as a leader in railroad investments. He went on to finance several important deals, including the consolidation of Thomas Edison’s electric companies in 1892 to form General Electric Company.
In 1895, Drexel, Morgan & Co. was reorganized and became J.P. Morgan & Company, a name that would become synonymous with Wall Street and global finance.
However, in 1933, the provisions of the Glass-Steagall Act forced J.P. Morgan & Co. to separate its investment banking from its commercial banking operations. As a result, two J.P. Morgan partners founded Morgan Stanley in 1935. These partners were Henry S. Morgan (son of J.P Morgan Jr.) and Harold Stanley. In the beginning, its headquarters were just down the street from J.P. Morgan.
In 1940, J.P. Morgan & Co. became J.P. Morgan & Co. Incorporated, and two years later, in 1942, J.P. Morgan & Co. went public. J.P. (Jack) Morgan, Jr. was its first chairman. However, he died only a year later.
In 1959, J.P. Morgan merged with the Guaranty Trust Company of New York, forming the Morgan Guaranty Trust Company.
In 1989, the U.S. Federal Reserve granted J.P. Morgan & Co. the right to underwrite and deal in corporate debt securities as a relaxation of the Glass-Steagall banking laws separating commercial and investment bank activities. This allowed the bank to get back to its investment banking roots.
The final chapter of J.P.Morgan & Co was written in 2000 when the company merged with Chase Manhattan, creating the new bank named J.P. Morgan Chase & Co.
Chase Manhattan Bank
Chase Manhattan Bank was formed in 1955 through the merger of the Chase National Bank and the Bank of The Manhattan Company.
In 1996, the bank became even bigger by merging with the Chemical Banking Corporation in one of the largest consolidations in U.S. banking history. Despite the acquiring bank being Chemical Banking Corp., Chase’s name was retained.
The turn of the millennium saw yet another merger, this time with J.P. Morgan & Co. in 2000. The two financial giants merged to create JPMorgan Chase & Co., a new behemoth in the world of banking.
JPMorgan Chase & Co.
The story of JPMorgan Chase began in the year 2000 when two of the most prominent banks in America, J.P. Morgan & Co. and The Chase Manhattan Corporation, merged to form a financial behemoth. This merger resulted in the formation of a new entity named J.P. Morgan Chase & Co.
In 2004, JPMorgan Chase grew bigger with the acquisition of Bank One Corp. The deal brought Jamie Dimon, the then Chairman and CEO of Bank One, on board as President and COO of JPMorgan Chase.
In 2005, James Dimon was named the CEO of JPMorgan Chase, and in 2006, he became its Chairman. Jamie Dimon’s connections and political clout helped the company become even bigger during the 2008 crisis by absorbing Bear Sterns and Washington Mutual.
A similar situation happened in 2023 when James Dimon managed to do a very favorable deal with the government to acquire The First Republic Bank, which was seized by the regulators just days before
📅 JPMorgan Chase’s History Timeline
These are selected events from JPMorgan Chase’s history. Timeline is broken down into parts that represent core company predecessors:
The “Bank” of the Manhattan Company
- 1799: The Manhattan Company was founded to supply “pure and wholesome” drinking water, but in a few months, opens The Bank of The Manhattan Company became the second commercial bank in New York City. One of the founders was Aaron Burr, the man who killed Alexander Hamilton, one of the founders of the Bank of New York.
- 1804: Manhattan Company founder Aaron Burr challenges Alexander Hamilton to a duel, resulting in Hamilton’s death.
- 1955: Chase National Bank merges with The Bank of The Manhattan Company to form Chase Manhattan Bank.
Chase National Bank
- 1877: Chase National Bank was founded by John Thompson and named in honor of Salmon P. Chase, Secretary of the Treasury under Abraham Lincoln and architect of the National Banking System.
- 1923: Chase National Bank was established in China.
- 1930: The Chase National Bank acquired Equitable Trust Company of New York in 1930, the largest stockholder of which was John D. Rockefeller, Jr., making Chase the largest bank in the US and the world.
- 1940s: Chase National Bank made a deal with Nazi Germany, which helped the German government exchange marks and likely originated from the forced sale of assets by Jewish refugees.
- 1947: Chase National Bank establishes a branch in Japan and the first post-war U.S. bank branch in Germany.
- 1955: Chase National Bank merges with The Bank of The Manhattan Company to form Chase Manhattan Bank.
Chase Manhattan Bank
- 1955: Chase Manhattan Bank was formed by the merger of Chase National Bank and The Bank of The Manhattan Company.
- 1958: Chase Manhattan introduces the Chase Manhattan Charge Plan, the first New York City bank to offer a retail credit account.
- 1973: Chase Manhattan establishes a representative office in Moscow, the first U.S. bank to have a business presence there since the 1920s.
- 1974: David Rockefeller, chairman of Chase Manhattan Bank, established the Chase Manhattan Bank Archives in an effort to preserve the legacy of his firm.
- 1996: Chase Manhattan Corporation merges into Chemical Banking Corporation in one of the largest consolidations in U.S. banking history. Despite the fact that acquiring bank was Chemical Banking Corp., the bank adopted the name Chase’s name.
- 2000: More than fifty years after the ties between Chase and Nazi Germany were revealed during Congressional hearings, Chase Manhattan publicly acknowledged the deal its predecessor Chase National Bank made with Nazi Germany.
- 2000: J.P. Morgan & Co. and The Chase Manhattan Corporation merged to form JPMorgan Chase & Co.
J.P. Morgan & Co.
- 1854: Junius S. Morgan, the patriarch of the Morgan banking family, moves to London and joins George Peabody & Co., which becomes the leading marketer of American securities in England and Europe, raising capital for important deals.
- 1864: J. Pierpont Morgan (son of Junius Morgan) founded his own firm with a cousin, J. Pierpont - Morgan & Company, which later became Dabney, Morgan & Co. and then “Drexel, Morgan & Co.” in 1871.
- 1871: J. Pierpont Morgan partners with Philadelphia banker Anthony Drexel to form Drexel, Morgan & Co., a private merchant banking house in New York City, which builds his reputation as a leader in railroad investments.
- 1882: The Drexel, Morgan & Co. building at 23 Wall Street is the first office building in New York City to draw power from the Edison Electric Illuminating Company’s newly built electric generating station.
- 1892: Drexel, Morgan & Co. financed the consolidation of Thomas Edison’s electric companies with the Thomson-Houston Electric Company to form General Electric Company.
- 1895: Drexel, Morgan & Co. reorganized in 1895 and became J.P. Morgan and Company
- 1901: J.P. Morgan & Co. organizes the buyout of industrialist Andrew Carnegie and combines some 15 companies to create United States Steel, the world’s first billion-dollar corporation.
- 1904: J.P. Morgan & Co. helps finance the Panama Canal.
- 1913: J. Pierpont Morgan dies, J.P. (Jack) Morgan, Jr. becomes senior partner of J.P. Morgan & Co.
- 1914: During WWI, J.P. Morgan & Co. loaned about $1.5 billion to the Allies to fight against the Germans and invested in the suppliers of war equipment to Britain and France, thus profiting from the financing and purchasing activities of the two European governments.
- 1920: A bomb exploded in front of the headquarters of J.P. Morgan Inc. at 23 Wall Street, injuring 400 and killing 38 people, and the FBI rendered the file inactive in 1940 without ever finding the perpetrators.
- 1933: The provisions of the Glass–Steagall Act forced J.P. Morgan & Co. to separate its investment banking from its commercial banking operations. As a result, in 1935, two J.P. Morgan partners, Henry S. Morgan (son of J.P Morgan Jr.) and Harold Stanley, founded Morgan Stanley. At the beginning, its headquarters were at 2 Wall Street, just down the street from J.P. Morgan.
- 1940: J.P. Morgan & Co. becomes J.P. Morgan & Co. Incorporated
- 1942: J.P.Morgan & Co. goes public. J.P. (Jack) Morgan, Jr. became the new corporation’s first chairman but died a year later.
- 1959: J.P. Morgan merged with the Guaranty Trust Company of New York to form the Morgan Guaranty Trust Company.
- 1969: J.P. Morgan & Co. was created as a bank holding company, with Morgan Guaranty Trust as the main subsidiary.
- 1989: In a relaxation of the Glass-Steagall banking laws separating commercial and investment bank activities, the U.S. Federal Reserve grants J.P. Morgan & Co. the right to underwrite and deal in corporate debt securities.
- 1998: J.P. Morgan openly discussed the possibility of a merger with banks such as Goldman Sachs, Chase Manhattan Bank, Credit Suisse, and Deutsche Bank AG.
- 2000: J.P. Morgan & Co. Incorporated merges with The Chase Manhattan Corporation. The new firm is named J.P. Morgan Chase & Co.
JPMorgan Chase
- 2000: J.P. Morgan & Co. Incorporated merges with The Chase Manhattan Corporation. The new firm is named J.P. Morgan Chase & Co.
- 2001: Bank paid out over $2 billion in fines and legal settlements for their role in financing Enron Corporation by aiding and abetting Enron Corp.’s securities fraud, which collapsed amid a financial scandal in 2001.
- 2002: Chase paid fines totaling $80 million, with the amount split between the states and the federal government. The fines were part of a settlement involving charges that ten banks, including Chase, deceived investors with biased research.
- 1994: JPMorgan Chase’s subsidiary acquired a 40% equity interest in Petron Corporation, the largest crude oil refiner and marketer in the Philippines.
- 2004: JPMorgan Chase merged with Chicago-based Bank One Corp., bringing on board current chairman and CEO of Bank One Jamie Dimon as president and COO of the combined company.
- 2005: JPMorgan Chase acknowledged that its two predecessor banks had received ownership of thousands of slaves as collateral prior to the Civil War. The company apologized for contributing to the “brutal and unjust institution” of slavery. The bank paid $5 million in reparations in the form of a scholarship program for Black students.
- 2005: JPMorgan Chase, which helped underwrite $15.4 billion of WorldCom’s bonds, agreed in March 2005 to pay $2 billion; that was 46 percent, or $630 million, more than it would have paid had it accepted an investor offer in May 2004 of $1.37 billion.
- 2005-12-31 James Dimon became the CEO of JPMorgan Chase.
- 2006: JPMorgan Chase acquired Bank of New York Mellon’s retail and small business banking network.
- 2006-12-31: James Dimon was named Chairman of JPMorgan Chase.
- 2008: JPMorgan Chase & Co. acquired Bear Stearns Companies Inc, which was close to bankruptcy.
- 2008: The U.S. government invested $25 billion in JPMorgan Chase under the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act, and the bank holding company Washington Mutual, Inc. was seized by the government and sold to JPMorgan Chase.
- 2009: JPMorgan Chase & Co. agreed to a $722 million settlement with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission to end a probe into the sales of derivatives that allegedly contributed to the near-bankruptcy of the Jefferson (Alabama) county.
- 2010: J.P. Morgan acquires full ownership of the firm’s U.K. joint venture, J.P. Morgan Cazenove, with origins dating to 1823.
- 2012: JPMorgan Chase & Co was charged for misrepresenting and failing to disclose that the CIO had engaged in speculative trades that exposed JPMorgan to significant losses.
- 2012: JPMorgan Chase & Co agreed to a historic settlement with the federal government and 49 states. The settlement, known as the National Mortgage Settlement (NMS), required the servicers to provide about $26 billion in relief to distressed homeowners and in direct payments to the states and federal government. This settlement amount makes the NMS the second-largest civil settlement in U.S. history, only trailing the Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement.
- 2012-04-13: Jamie Dimon dismissed press accounts of possible losses in the bank’s London Whale scandal as a “tempest in a teapot”.
- 2012-05: An investment unit of JPMorgan Chase announced a loss of $2 billion through a complex series of trades in derivatives, including credit-default swaps (CDSs). Even was referred to as the London Whale scandal.
- 2013: JPMorgan Chase agreed to pay a total of $920 million in fines and penalties to American and UK regulators for violations related to the credit derivatives trading loss and other incidents
- 2013: JPMorgan Ventures Energy Corporation (JPMVEC), a subsidiary of JPMorgan Chase & Co., agreed to pay $410 million in penalties and disgorgement to ratepayers for allegations of market manipulation stemming from the company’s bidding activities in electricity markets in California and the Midwest.
- 2013: JPMorgan Chase agreed to pay $13 billion to settle investigations into its business practices pertaining to mortgage-backed securities. Of that amount, $9 billion was penalties and fines, and the remaining $4 billion was consumer relief. Conduct at Bear Stearns and Washington Mutual prior to their 2008 acquisitions accounted for much of the alleged wrongdoing.
- 2014: JPMorgan Chase agreed to pay a total of $2.05 billion in fines and penalties to settle civil and criminal charges related to its role in the Madoff scandal.
- 2016: JPMorgan Chase agreed to pay $264 million in fines to settle civil and criminal charges involving a systematic bribery scheme spanning 2006 to 2013 in which the bank secured business deals in Hong Kong by agreeing to hire hundreds of friends and relatives of Chinese government officials, resulting in more than $100 million in revenue for the bank.
- 2017: J.P. Morgan was sued by Nigeria for $875 million, alleged to have been transferred to a corrupt former minister.
- 2018: As part of an investigation by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) into abusive practices related to American depositary receipts (ADRs), JPMorgan agreed to pay more than $135 million to settle charges of improper handling of “pre-released” ADRs without admitting or denying the SEC’s findings.
- 2020-03: Jamie Dimon underwent “emergency heart surgery.”
- 2020: J.P. Morgan settled with the U.S. for $920 million in manipulating precious metals futures and government bond markets.
- 2021: JPMorgan Chase launched an app-based current account under the Chase brand in the UK.
- 2022: Two women who accused Jeffrey Epstein of sex trafficking and sexual abuse also sued JPMorgan and Deutsche Bank, accusing them of benefiting and closing their eyes to Epstein’s sex trafficking operations. According to the lawsuits, banks knew that Epstein’s accounts were used to finance sex trafficking crimes.
- 2022: Two women who accused Jeffrey Epstein of sex trafficking and sexual abuse also sued JPMorgan and Deutsche Bank, accusing them of benefiting and closing their eyes to Epstein’s sex trafficking operations. According to the lawsuits, banks knew that Epstein’s accounts were used to finance sex trafficking crimes.
- 2023: JPMorgan Chase struck a deal to buy most of the operations of First Republic Bank, shortly after regulators seized it. As part of the deal, JPMorgan got quite favorable terms, including financing and a backstop on certain future losses.
📚 Recommended Articles & Other Resources
Who Owns Berkshire Hathaway: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Visual overview of who owns Berkshire Hathaway and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Apple: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Visual overview of who owns Apple and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Paypal: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns PayPal and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Visa: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Visa and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth..
Who Owns Exxon Mobil: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Exxon Mobil and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Who Owns Netflix: The Largest Shareholders Overview
Overview of who owns Netflix and who controls it. With a list of the largest shareholders and how much is each of their stake worth.
Other Resources
- JPMorgan Chase’s Annual Financials Statements (K-10)
- JPMorgan Chase’s Proxy Statement
- JPMorgan Chase’s Certificate of Incorporation
Disclaimer: Although I use third-party trademarks and logos in this article and its visuals, kamilfranek.com is an independent site, and there is no relationship, sponsorship, or endorsement between this site and the owners of those trademarks.

